* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Body Has Methods of Protecting Itself from Diseases
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Anti-nuclear antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
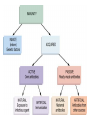
The Body Has Methods of Protecting Itself from Diseases Immune Response • • 1st Defense is the Skin and Mucus 2nd Defense occurs when injured cells release chemicals that increase blood flow to an area (cut or scrape). The blood brings Macrophage: a white blood cell that engulfs and kills pathogens • 3rd Defense macrophages along with T cells and B cells attach and kill infected cells. Treating Diseases • Antibiotic: will kill or inhibit the growth/reproduction of microorganisms Do Not effect viruses Lymphatic System: produces white blood cells and antibodies 2 types of White Blood Cells (1) T cells and (2) B cells Antibody Immunity (see p. 1037) • Antigens: foreign substances that stimulate an immune response • Antibodies: proteins in the blood that correspond to an antigen • B cells make antibodies • T cells kill infected cells • Helper T cells help B cells make antibodies • Memory cells are ready and armed to respond rapidly if the same pathogen invades the body at a later time Passive and Active Immunity (p.1039) • Passive Immunity: • Active Immunity: • Acquiring antibodies produced in someone else, such as through an injection or a mother passing them through the placenta or milk to her fetus. • Ex. Person bite by a snake…injected w/antibodies from a horse that is immune to the snake venom • Due to a person forming his or her own antibodies after being exposed to an antigen • Vaccine: Weakened, dead or incomplete pathogens/antigens injected into body to cause and immune response.