* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TOLERANCE
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
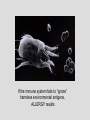
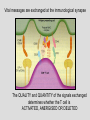
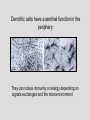
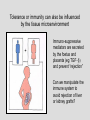
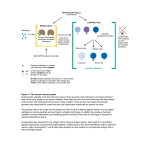
TOLERANCE Deletion, anergy or ignorance? Normal thyroid Diseased thyroid If the immune system fails to “delete” or anergise tissue reactive lymphocytes, AUTOIMMUNITY occurs If the immune system fails to “ignore” harmless environmental antigens, ALLERGY results TO COMBAT THE DIVERSITY OF PATHOGENIC ANTIGENS THAT MIGHT BE ENCOUNTERED BY THE HOST, THE IMMUNE SYSTEM MUST PRODUCE POPULATIONS OF LYMPHOCYTES WITH RECEPTORS OF EQUAL DIVERSITY To achieve this, the antigen receptors of T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes are generated randomly. This repertoire will inevitably contain lymphocytes specific for self antigen. The body must therefore distinguish between self and non-self determinants to avoid autoimmunity, and between dangerous and non-dangerous antigen to avoid allergy. HOW IS THIS ACHIEVED? • “Central tolerance” edits lymphocytes BEFORE they enter the circulation as naïve cells • “Peripheral tolerance” acts as a back up to eliminate potentially autoreactive lymphocytes AFTER they enter the circulation. • Some cells are DELETED, some cells are ANERGISED. • ANERGIC cells can be re-activated if a “DANGER” signal is encountered Central tolerance occurs in the thymus where T cells are edited before they enter the circulation as naïve cells Clonal selection theory also applies to B lymphocytes that are “edited” in the bone marrow and lymph nodes T CELLTOLERANCE IS ESSENTIAL TO CONTROL POTENTIAL B CELL AUTOREACTIVITY B cells need T cell “help” to make high affinity antibody Dendritic cells control T cell immuno-reactivity and help decide the fate of the T cell Vital messages are exchanged at the immunological synapse The QUALITY and QUANTITY of the signals exchanged determines whether the T cell is ACTIVATED, ANERGISED OR DELETED Quantity of antigen is also important: lymphocytes specific for abundant self-antigen are deleted, low level self-antigen is “ignored” Dendritic cells have a sentinel function in the periphery: They can induce immunity or anergy depending on signals exchanged and the microenvironment The “DANGER HYPOTHESIS” Dendritic cells have receptors that recognise pathogens and inflammatory mediators released by other cells. These “danger signals help the DC activate T cells and stimulate protective immunity Therefore antigens encountered in the absence of infection or injury are NOT dangerous and induce tolerance Tolerance or immunity can also be influenced by the tissue microenvironment Immuno-suppressive mediators are secreted by the foetus and placenta (eg TGF-b) and prevent “rejection” Can we manipulate the immune system to avoid rejection of liver or kidney grafts? SUMMARY To combat the diversity of pathogenic antigens that might be encountered by the host, the immune system must produce populations of lymphocytes with receptors of equal diversity • To achieve this, the antigen receptors of T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes are generated randomly. • This repertoire will inevitably contain lymphocytes specific for self antigen. • The body must therefore distinguish between self and non-self determinants to avoid AUTOIMMUNITY, • and between dangerous and non-dangerous antigen to avoid ALLERGY. • “Central tolerance” edits lymphocytes BEFORE they enter the circulation as naïve cells • “Peripheral tolerance” acts as a back up to eliminate potentially autoreactive lymphocytes AFTER they enter the circulation. • Some cells are DELETED, some cells are ANERGISED. • ANERGIC cells can be re-activated if a “DANGER” signal is encountered Dendritic cells are vital in the process and decide whether tolerance or immunity to an antigen will occur Can the immune response and dendritic cells be manipulated to reinduce tolerance in autoimmunity or to prevent graft rejection?