* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.-LYMPHOCYTE-info
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
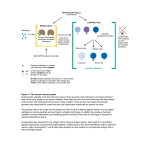
B lymphocytes Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell. There are a number of different types of lymphocyte; two of the most important are B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes. B lymphocytes are also called B cells. They are formed in the bone marrow of mammals. B lymphocytes play an important role in the humoral immune system. B cells play three important roles in the immune response: 1. 2. 3. they produce antibodies in response to specific antigens they perform the role of antigen-presenting cells they develop into memory B cells. Production of antibodies Each B cell can produce a specific antibody that can recognise a specific antigen from a pathogen or toxin. The antibody will bind to the antigen, forming an antigen – antibody complex. The antigen–antibody complex has two modes of action: It may inactivate the pathogen/toxin, rendering it susceptible to phagocytosis. It may stimulate a response, resulting in cell lysis. Antigen-presenting cells B cells can identify specific antigens and present them to T cells. T cells can then destroy the pathogen. Memory B cells Memory B cells exist long after the infection has subsided. Should the same antigen reappear in later life the memory B cells will be on hand to stimulate the appropriate immune response. T lymphocytes Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell. There are a number of different types of lymphocyte; two of the most important are B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes. T lymphocytes are also called T cells. They are formed in the thymus gland – hence their name. T lymphocytes play an important role in the immune system and they account for more than four -fifths of circulating lymphocytes. There are two main groups of T lymphocytes: cytotoxic T cells and helper T cells. Cytotoxic T cells The cytotoxic T cells are also called killer T cells. They recognise antigens on infected cells, bind to the antigen and can destroy the cells by apoptosis. Apoptosis is a form of programmed cell death – the cell is instructed to destroy itself. Once cytotoxic T cells have completed their job, the majority of cells undergo apoptosis. However, a few cells become ‘memory cells’, which will remain on hand to respond should the antigen reappear at some point in the future. Helper T cells Helper T cells are not able to destroy infected cells. Instead they produce cytokines – a chemical signal that activate B lymphocytes and phagocytes, which can then act to destroy the infected cell.