* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TCR
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
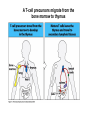
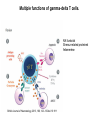
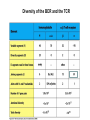
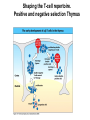
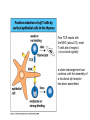
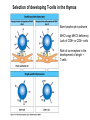
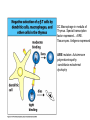
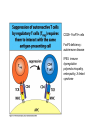
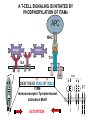
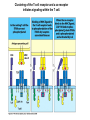
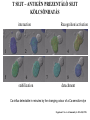
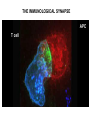
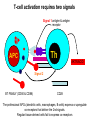
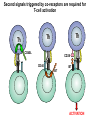
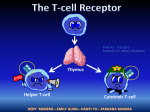
T-cell development and differentiation T-cell diversity is generated in the thymus The TCR is a recognition unit that looks like an arm of the BCR In which the μ and β chains, and the light chains and the α-chains are homologuos The main mechanisms of gene rearrangements are similar for the TCR and BCR CDR1,2, 3, loops in theTCRα and TCRβ chains A T-cell precursors migrate from the bone marrow to thymus T-cell markers are induced after thymocytes interact with the thymic epithelial cells A Notch-1receptor and its cytoplasmic region, acting as a transcription factor is required for the development of the T-cell lineage Az αβ and γδ T-cells recognize different antigens Less V-segments, but the Delta-chain has large junctional diversity Vg9Vd2 T cells can recognize PAgs (such as isopentenyl pyrophosphate, IPP) that are accumulated in tumour cells Pags: natural phospho-antigens 1-5 % of T-cells in the blood But γδ T-cells are the dominant type in epithelia Unlike αβ T-cells recognition of antigens by γδ T-cells is independent of MHC. They recognize phosphorylated metabolites produced by many microbes. Tumor-specific immune response Multiple functions of gamma-delta T cells. NK funkciók Stressz-related proteinek felismerése British Journal of Haematology, 2013, 160, 123–132 doi:10.1111 Generation of T-cell receptor diversity mehanizmusa (occurs in the thymus) Si milar to that of B cells’… BUT!! 1. No diversification after activation 2. No secreted form Diversity of the BCR and the TCR The αβ and γδ T-cell lineages develop from a common precursor A TCR-rearrangement—similar to BCR A β-chain rearrangement (like Ig heavy chain) Efficiency of beta chain rearrangement is about 80% RAG-1 RAG-2 genes become are inactivated Timocyte proliferation CD4, CD8 expressionó TCR-rearrangement is similar to that of the BCR The α-Chain rearrangement (Ig light chain) B- AND T-CELL RECEPTORS SHARE BASIC STRUCTURE mIg H mIg L TCR T cell receptor TCR V TCR C TCR = + The variable region of the -chain is generated by gene rearrangements of the V – D – J gene segments analogous to the generation of IgH diversity The variable region of the -chain is generated by the recombination of V and J analogous to IgL T-CELL Single binding C site No somatic mutation Main steps of T-cell development, gene rearrangemnts, changes in gene expression Shaping the T-cell repertoire. Positive and negative selection Thymus Few TCR reacts with the MHC (about 2%) most T-cells die of neglect. ( no survival signals) α-chain rearrangement can continue until the assembly of a functional αβ receptor has been assembled. Selection of developing T-cells in the thymus Bare lymphocyte syndrome MHCI vagy MHCII deficiency Lack of CD8+ or CD4+ cells Role of co-receptors in the development of single + T-cells DC Macrophage in medulla of Thymus. Special transcription factor expressed… AIRE. Tissue spec. Antigens expressed AIRE mutaton: Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy -candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy Multiple stages of T-cell development in the thymus CD25+ FoxP3+ cells FoxP3-deficiency: autoimmune disease IPEX: immune dysregulation polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome T-cell activation Characteristics of antigen recognition by T-cells (TCR) 1. T-cells need antigen processing by APCs 2. T-cells recognize virus-infected cells APC ANTIGEN BINDING NO INTERACTION T CELL AKTIVATION Antigén receptor B-CELL T-CELL (review) Phases of T cell response A T-CELL SIGNALING IS INITIATED BY PHOSPHORYLATION OF ITAMs APC MHC Antigen Antigen TCR BCR αβ s V s s sV s C s s sC ss P P D/E X7 D/E X2 YXXL/I X7 YXXL/I ITAM Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motif ACTIVATION CD3 CD3 εδ s s s s εγ s s s s ζζ s s Clustering of the T-cell receptor and a co-receptor initiates signaling within the T cell. (review) TCR signaling THE IMMUNOLOGICAL SYNAPSE APC T APC T SEJT T SEJT – ANTIGÉN PREZENTÁLÓ SEJT KÖLCSÖNHATÁS interaction Recognition/activation 1 2 3 4 5 6 stabilization 7 8 detachment Ca-influx detectable in minutes by the changing colour of a Ca-sensitive dye Negulescu P.A. et. al. Immunity 4: 421-430, 1996 AZ IMMUNOLOGICAL SYNAPSEÓGIAI SZINAPSZIS ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELL ICAM-1 B7 CD48 CD4 CD2 CD28 adaptor LFA-1 SIGNALING COMPLEX T SCELL ACTIVATED T CELL THE IMMUNOLOGICAL SYNAPSE APC T cell CELL ADHESION AND SIGNALING IS FACILITATED BY MANY RECEPTORLIGAND INTERACTIONS C D2 3 (Fc eRII) CD8 1 (TAPA) C D2 1 (CR2 ) CD 19 C d 7 9b C d 7 9a sIgM MHCI – CD8 MHCII – CD4 CD40 – CD40L BCR B7 – CD28 C D43 C D11 a /1 8 (LFA- 1) C D5 4 (IC AM-1 ) CD 10 2 (IC AM-2 ) C D5 0 (IC AM-3 ) CD 40 APC CD 22 CD 72 C D45 RO ? * T CELL C D5 CD4 M HC II M HCI * C D15 4 (C D4 0 L) TCR * C D3 C D58 ( LFA-3 ) CD 59 CD8 C D 8 0 (B7 - 1 ) C D 8 6 (B7 - 2 ) C D2 CD 20 C D 28 * * C D 1 5 2 ( C TLA- 4 ) C D1 06 ( VC AM) C D49 d /2 9 (VLA-4 ) * T-cell activation requires two signals Signal 1 antigén & antigén receptor Th APC AKTIVÁCIÓ Signal 2 B7 FAMILY (CD80 & CD86) CD28 The professional APCs (dendritic cells, macrophages, B-cells) express or upregulate co-receptors that deliver the 2nd signals. Regular tissue-derived cells fail to express co-receptors Second signals triggered by co-receptors are required for T-cell activation Th Th Th CD40L CD28 CD40 B7 B7 ACTIVATION