* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10 General anatomy of immune system
Survey
Document related concepts
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
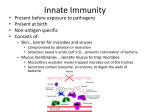
1 General anatomy of the IMMUNE SYSTEM ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM • The immune system is localized in several parts of the body – immune cells develop in the primary organs bone marrow and thymus (yellow) – immune responses occur in the secondary organs (blue) 2 3 ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM 4 • Thymus – glandular organ near the heart – where T cells learn their jobs • Bone marrow – blood-producing tissue located inside certain bones – blood stem cells give rise to all of the different types of blood cells • Spleen – serves as a filter for the blood – removes old and damaged red blood cells – removes infectious agents and uses them to activate cells called lymphocytes • Lymph nodes – small organs that filter out dead cells, antigens, and other “stuff” to present to lymphocytes • Lymphatic vessels – collect fluid (lymph) that has “leaked” out from the blood into the tissues and returns it to circulation PASSIVE IMMUNITY While your immune system was developing, you were protected by immune defenses called antibodies. These antibodies traveled across the placenta from the maternal blood to the fetal blood. Antibodies (Y) are also found in breast milk. The antibodies received through passive immunity last only several weeks. 5 reign invaders - viruses, bacteria, allergens, toxins and 6 rasites- constantly bombard our body. YOUR ACTIVE IMMUNE DEFENSES Innate Immunity Adaptive Immunity - invariant (generalized) - early, limited specificity - the first line of defense - variable (custom) - later, highly specific - ‘‘remembers’’ infection INNATE IMMUNITY When you were born, you brought with you several mechanisms to prevent illness. This type of immunity is also called nonspecific immunity. Innate immunity consists of: • Barriers • Cellular response – phagocytosis – inflammatory reaction – NK (natural killer) and mast cells • Soluble factors 7 8 INNATE IMMUNITY Barriers • Physical – skin – hair – mucous • Chemical – – – – – sweat tears saliva stomach acid urine 9 INNATE IMMUNITY Cellular response • nonspecific - the same response works against many pathogens • this type of response is the same no matter how often it is triggered • the types of cells involved are macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer cells, and mast cells • a soluble factor, complement, is also involved 10 Phagocytic cells include: Macrophages engulf pathogens and dead cell remains Neutrophils release chemicals that kill nearby bacteria • pus = neutrophils, tissue cells and dead pathogens 11 Phagocyte migration CELLS alive! Neutrophils and macrophages recognize chemicals produced by bacteria in a cut or scratch and migrate "toward the smell". Here, neutrophils were placed in a gradient of a chemical that is produced by some bacteria. The cells charge out like a "posse" after the bad guys. 12 Macrophages • WBCs that ingest bacteria, viruses, dead cells, dust • most circulate in the blood, lymph and extracellular fluid • they are attracted to the site of infection by chemicals given off by dying cells • after ingesting a foreign invader, they “wear” pieces of it called antigens on their cell membrane receptors – this tells other types of immune system cells what to look for 13 Macrophage and E. coli ©Dennis Kunkel Microscopy, Inc., www.DennisKunkel.com 14 Macrophage ingesting yeast CELLS alive! This human macrophage, like the neutrophil, is a professional "phagocyte" or eating cell (phago = "eating", cyte = "cell"). Here, it envelops cells of a yeast, Candida albicans. After ingestion, the white cell must kill the organisms by some means, such as the oxidative burst. 15 Neutrophils • WBCs – are phagocytic, like macrophages • neutrophils also release toxic chemicals that destroy everything in the area, including the neutrophils themselves Neutrophil phagocytosing S. pyogenes, the cause of strep throat 16 CELLS alive! Human neutrophils are WBCs that arrive quickly at the site of a bacterial infection and whose primary function is to eat and kill bacteria. This neutrophil ingesting Streptococcus pyogenes was imaged in gray scale with phase contrast optics and colorized. 17 Neutrophil killing yeast NEUTROPHIL YEAST CELLS alive! One way that neutrophils kill is by producing an antibacterial compound called “superoxide anion“, a process called oxidative burst. Here, an amoeboid human neutrophil senses, moves toward and ingests an ovoid yeast. In the next two panels, oxidation can be seen by using a dye, and is colorized here. INNATE IMMUNITY Cellular response Complement • complement is not a cell but a group of proteins • these proteins circulate in the blood • complement plays a role in inflammatory responses of both the innate and adaptive immune responses 18 INNATE IMMUNITY Cellular response Complement • complement is not a cell but a group of proteins • these proteins circulate in the blood – help to recruit phagocytes to site of inflammation and activate them – bind to receptors on phagocytes, helping to remove agent of infection – form pores in the invader or infected cell’s membrane (like the NKs do) – activate mast cells to release histamine and other factors • complement plays a role in inflammatory responses of both the innate and adaptive immune responses 19 20 INNATE IMMUNITY Cellular response Inflammatory response • chemical and cell response to injury or localized infection • eliminates the source of infection • promotes wound healing Step 1. Circulation to the site increases tissue warm, red and swollen Step 2. WBCs leak into tissues phagocytes engulf and destroy bacteria 21 INNATE IMMUNITY Cellular response Inflammatory response (cont’d) The release of histamine and prostaglandin causes local vessel dilation resulting in: • more WBCs to site • increased blood flow redness and warmth • increased capillary permeability • phagocytes move out of vessels into intracellular fluid (ICF) • edema (swelling) due to fluids seeping from capillaries INNATE IMMUNITY Cellular response Inflammatory response (cont’d) Fevers have both positive and negative effects on infection and bodily functions POSITIVE NEGATIVE • indicate a reaction to infection • extreme heat enzyme denaturation and interruption of normal biochemical reactions • stimulate phagocytosis • slow bacterial growth – increases body temperature beyond the tolerance of some bacteria – decreases blood iron levels > 39° C (103°F) is dangerous > 41°C (105°F) could be fatal and requires medical attention 22 23 Natural killer cells (NK cells) • instead of attacking the invaders, they attack the body’s own cells that have become infected by viruses • they also attack potential cancer cells, often before they form tumors • they bind to cells using an antibody “bridge”, then kill it by secreting a chemical (perforin) that makes holes in the cell membrane of the target cell. With enough holes, the cell will die, because water rushing inside the cell will induce osmotic swelling, and an influx of calcium may trigger apoptosis. 24 Mast cells • are found in tissues like the skin, near blood vessels. • are activated after antigen binds to a specific type of antibody called IgE that is attached to receptors on the mast cell. • activated mast cells release substances that contribute to inflammation, such as histamine. • mast cells are important in allergic responses but are also part of the innate immune response, helping to protect from infection. 25 INNATE IMMUNITY – Soluble factors • Interferon – a chemical (cytokine) produced by virus-infected cells that contributes to their death by apoptosis • Acute phase proteins – proteins in the plasma that increase during infection and inflammation – can be used diagnostically to give an indication of acute inflammation 26 Apoptosis or cell death CELLS alive! Human neutrophils released into the blood "commit suicide“ after only 1 day. A neutrophil (left) undergoes apoptosis, a series of changes including violent membrane blebbing and fragmentation of DNA. Apoptotic cells break into smaller pieces called apoptotic bodies that other body cells recognize and eat. 27 • Your mom’s antibodies were effective for just a short time at birth, but your innate immune system can be activated quickly. It is always your first line of defense during an infection, but it can’t always eliminate the germ. • When this happens, your body initiates a focused attack against the specific pathogen that is causing the infection. This attack may lead to long-term protection against that pathogen. • This type of immunity is called adaptive immunity, the customized second line of defense. reign invaders - viruses, bacteria, allergens, toxins and rasites- constantly bombard our body. 28 YOUR ACTIVE IMMUNE DEFENSES Innate Immunity Adaptive Immunity - invariant (generalized) - early, limited specificity - the first line of defense - variable (custom) - later, highly specific - ‘‘remembers’’ infection 1. Barriers - skin, tears 2. Phagocytes - neutrophils, macrophages 3. NK cells and mast cells 4. Complement and other proteins 29 This immunology curriculum and integrated laboratory modules were created by teachers and scientists working together through a grant from the National Science Foundation to the Nanobiotechnology Center in collaboration with the Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers, which is funded by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. Collaborators for this project: Harriet Beck, Wellsville Central School Jim Blankenship, Cornell Institute for Biology Teachers Rita Calvo, Cornell University Jerrie Gavalchin, Cornell University Mary Kay Hickey, Dryden High School Susan Oliver, Dundee High School Jeanne Raish, Avoca Central School Anna Waldron, Nanobiotechnology Center This material is based upon work supported in part by the STC Program of the National Science Foundation under Agreement No. ECS-9876771. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation. 30 Permission to use images were secured by the NBTC from various sources: KUBY IMMUNOLOGY by Richard A. Golsby and Thomas J. Kindt and Barbara A. Osborne. © 1992, 1994, 1997, 2000 by W.H. Freeman and Company. Used with permission. © 2001 From Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease, Fifth edition by Charles A. Janeway, Paul Travers, Mark Walport and Mark Shlomchik. Reproduced by permission of Routledge, Inc., part of The Taylor & Francis Group. © 2000 From The Immune System by Peter Parham. Reproduced by permission of Routledge, Inc., part of The Taylor & Francis Group. Dennis Kunkel Microscopy, Inc., www.DennisKunkel.com CELLS alive! www.cellsalive.com Mike Clark, www.path.cam.ac.uk/~mrc7/