* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Immune System - Welcome to BioGleich
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
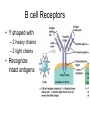
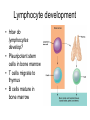
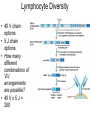
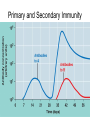
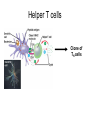
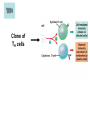
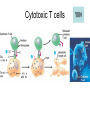
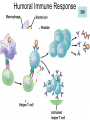
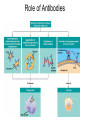
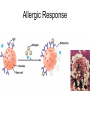
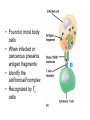
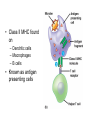
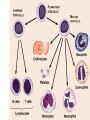
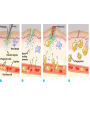
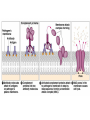
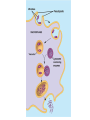
Immune System 1. Define the following: a. B cells b. T cells c. Macrophages 2. Provide 3 cells and/or molecules involved in specific defense. 3. Provide 3 cells and/or molecules involved in non-speccific defense. Innate Immunity • • • • What is innate immunity? Present from birth Non specific External – Skin – Mucous membranes • Internal – Macrophages – phagocytes Phagocytic cells • Phagocytes bind to non-self surface carbohydrates • microbe is engulfed forming a vacuole • lysosome fuses with vacuole • Evolution of microbes: – Extra capsule hides non-self surface carbohydrates – Resistant to destruction by lysosomes Pahgocytic Leukocytes • Neutrophils: most abundant – Phagocytes that engulf and destroy microbes – Self destruct pus • Monocytes: more effective – Macrophages – Reside mainly in lymph nodes, spleen and lymph tissues • Eosinophils: less abunadant limited role – Fight multicellular parasites • Dendritic cells: – Stimulate aquired immunity Antimicrobial Proteins • Complement system • Interferons – Secreted by virus infected cells – Induce other non-infected cells to release viral inhibitors • Defensins – Secreted by macrophages – Damage pathogens Responses • • • • Localized inflammatory response Fever Septic shock – systemic inflamation Natural killer cells – Attack cancer and virus-infected cells Lymphatic System Acquired Immunity Antigen Recognition • What are the two main types of lymphocytes? – B cells – T cells • There are antigen receptors on these cells • Antigen receptors are specific for an epitope B cell Receptors • Y shaped with – 2 heavy chains – 2 light chains • Recognize intact antigens T cell Receptors • Recognizes self/non self complexes – Pieces of antigens – MHC • Class I MHC • Class II MHC Lymphocyte development • How do lymphocytes develop? • Pleuripotent stem cells in bone marrow • T cells migrate to thymus • B cells mature in bone marrow Lymphocyte Diversity • 40 V chain options • 5 J chain options • How many different combinations of V/J arrangements are possible? • 40 V x 5 J = 200 • How do we avoid auto immune issues? • Before B cells and T cells mature, they are checked for class I and class II MHC compatibility. • If they are compatible they are destroyed Clonal Selection of Lymphocytes • B cells, TH, and TC cells may be activated by finding their antigen in the body • Binding of the antigen stimulated the cell to: – Generate short-lived clone of effector cells – Generate long-lived memory cells Primary and Secondary Immunity Humoral and Cell mediated Immunity Helper T cells Clone of TH cells Clone of TH cells Cytotoxic T cells Humoral Immune Response Antibodies Role of Antibodies Active and Passive Immunity • What is the difference between active and passive immunity? • Active immunity – Natural exposure to antigen – Immunization • Passive immunity – Transferred antibodies – Seen with pregnant and nursing women – Also with anti-venom injections Blood Groups • Why would a person with type A blood have anti – B antibodies? • There are bacteria with similar antigens • The immune response produced by blood group antigens has no memory • Blood mixing at birth causes no problems fro future pregnancies • Rh factors, however, do have memory so there is a problem here • How do Rh negative mothers deal with blood from Rh positive babies? Allergic Response Autoimmune Diseases • Found in most body cells • When infected or cancerous presents antigen fragments • Identify the self/nonself complex • Recognized by Tc cells • Class II MHC found on – Dendritic cells – Macrophages – B cells • Known as antigen presenting cells Macrophage ingesting a yeast cell Lining of trachea with orange mucus producing cells and yellow cilia