* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 22_SocialPsych2 - HomePage Server for UT Psychology
Solomon Asch wikipedia , lookup
Leon Festinger wikipedia , lookup
Social tuning wikipedia , lookup
Implicit attitude wikipedia , lookup
Introspection illusion wikipedia , lookup
Vested interest (communication theory) wikipedia , lookup
Albert Bandura wikipedia , lookup
Impression formation wikipedia , lookup
Social perception wikipedia , lookup
Elaboration likelihood model wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive dissonance wikipedia , lookup
Attitude (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
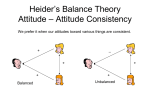
Introduction to Psychology Class 22: Social Psychology 2 Myers: 541-554 August 7, 2006 Attitude • A belief and feeling that predisposes one to respond in a particular way to objects, people, ideas, and events • So an attitude = cognition + emotion • Remember that predisposition + situation = behavior • Also see how attitudes -> behavior -> attitudes Measurement • Explicit or Overt measures - Self-reports - Bogus pipeline • Implicit or Covert Measures - Non-verbal behavior - Physiology; e.g. Facial EMG, BP - Reaction times; e.g. IAT Attitude change COGNITIVE CONSISTENCY: No attitude change Marriage Person A + Person B Diet Coke + Viewer + + Celebrity COGNITIVE INCONSISTENCY: Attitude change Marriage Person A + + Person B Diet Coke Viewer + + Celebrity Cognitive dissonance • The effect of counter-attitudinal behavior on original attitude (Leon Festinger) - $1 is “insufficient justification” for a lie (dissonance) - Participants infer that they must have liked the experiment (resolution of dissonance) - In the process, there is attitude change A Dissonance Classic 25 20 15 Reported Enjoyment 10 5 0 No Lie Lie for $1 Lie for $20 Routes to Persuasion Degree of elaboration - Motivation (high, low) - Opportunity (high, low) 1) Central (high M, high O) “So that is why he supports the policy in question…” 2) Peripheral (low M, low O) “Hm, he is rather charming…” Social Influence • Compliance Changes in behavior elicited by direct requests • Obedience Change in behavior produced by commands of authority • Conformity The tendency to change perceptions, opinions, or behavior in ways that are consistent with group norms Compliance: Robert Cialdini • Foot-in-the-door 2-step technique in which an influencer sets the stage for a real request by first getting a person to comply with a much smaller request • Door-in-the-face 2-step technique in which an influencer prefaces the real request with one so large that it is bound to be rejected Obedience: Stanley Milgram • Cults and mass suicides • War and violence Conformity: Solomon Asch Group Influences • Private vs. public conformity • Information vs. normative influence Other effects of others on behavior • • • • Social facilitation Social loafing Group polarization Groupthink Role-Playing: Phil Zimbardo • Stanford Prison Experiment • Ethical issues • Findings