* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Beyond Cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
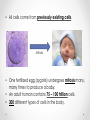
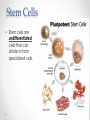
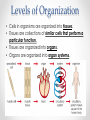
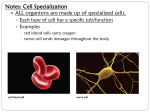
Tissues: Beyond Cells • All cells come from previously existing cells. Mitosis • One fertilized egg (zygote) undergoes mitosis many, many times to produce a baby. • An adult human contains 75 – 100 trillion cells. • 300 different types of cells in the body. • How does one fertilized egg develop into all of the different types of cells found in a human? fat cells bone cells skin cells muscle cells Answer: Cell Specialization • Specialized cells have physical and chemical differences that allow them to perform different functions • Red blood cells carry oxygen in the blood • Nerve cells transmit electrical impulses • Plant leaf cells perform photosynthesis • How did one cell give rise to so many different types of cells in one organism? Genes • Genes (base pair sequences) turn on and off to control the characteristics and functions of a cell. • Many factors influence what genes are turned on and off, including the environment and neighbouring cells. Stem Cells • Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can divide to form specialized cells. Levels of Organization • Cells in organisms are organized into tissues. • Tissues are collections of similar cells that perform a particular function. • Tissues are organized into organs. • Organs are organized into organ systems. • More than one kind of cell or tissue are found in any organ. • Different cells, tissues, organs and organ systems are found in animals and plants.