* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quantum Mechanics
Coherent states wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Bell test experiments wikipedia , lookup
Ensemble interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Many-worlds interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Orchestrated objective reduction wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum entanglement wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Wave function wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Wheeler's delayed choice experiment wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Path integral formulation wikipedia , lookup
Delayed choice quantum eraser wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
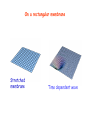
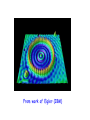
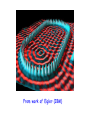
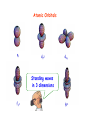
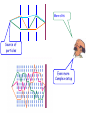
Good Evening to all of YOU! The strange (and beautiful) world of Quantum Mechanics Very frightening Just beautiful! Outline 1. Wave or Particle? ..Two slit experiments 2. Uncertainty Principle 3. Standing Waves 4. Stationary States - Atomic Orbitals 5. Do we understand Quantum Mechanics? 6. The Path Integral – Random Walk 7. The Copenhagen Interpretation 8. The Schroedinger’s Cat 9. The EPR Paradox Two Slit experiments With particles (bullets) I1 I2 I12 Behavior of bullets is easy to understand - LUMPINESS! With waves (water waves) I1 I2 I12 Waves interfere! NO LUMPINESS! 1 + 2 12 With electrons I1 I2 I I12 12 Electrons are like bullets - lumps LUMPINESS! INTERFERENCE! 1/1000 mm http://www.hqrd.hitachi.co.jp/em/doubleslit.cfm God does not play dice! This type of behavior was observed first in the case of light! History Light is a beam of particles Exhibits interference, hence waves! Huygens Newton EM Theory, hence waves Einstein In photoelectric effect, light behaves like particles In my scattering expts, light - beam of particles Compton Maxwell On Mondays, Wednesdays and Fridays, it is a PARTICLE! On, Tuesdays,Thursdays and Saturdays it is a WAVE! Oh LORD, please, is it a PARTICLE or a WAVE!!??? On Sundays It is both! It has a DUAL NATURE Not only electrons and photons,but EVERYTHING has this dual nature! Exptly shown for protons, neutrons, He atoms, even C60! C60 Prof. A. Zeilinger http://www.quantum.univie.ac.at/zeilinger/ Duality Whom do you see in this picture? A young girl? Old woman? De Broglie - Heisenberg de Broglie Heisenberg Reflection Modes of a String - Standing waves Standing waves of a bridge On a rectangular membrane Stretched membrane Time dependent wave Stretched membrane One node No nodes Two nodes Infinite modes One node Four nodes Box Particle in a box Standing wave patterns in 2D can be formed! From work of Eigler (IBM) From work of Eigler (IBM) From work of Eigler (IBM) Box + Hydrogen Atom: ebound to proton Standing wave patterns in 3D can be formed! Atomic Orbitals pz dz2 dxy Standing waves in 3 dimensions fz 3 gz4 leads to bonding Electron density goes into internuclear region! Constructive interference! Electron density goes away from the internuclear region! Destructive interference! Do we understand Quantum Mechanics? How does it know that both the slits are open!!?? I don’t understand it!! At least this time, he is sensible! Nobody does!!! Does it go through both the slits? How does an electron move (propagate)? Through all possible paths! He is crazy! More slits Source of particles Even more Complex setup In the limit of walls each with slits……. All paths contribute! Action Quantum mechanics and the drunken walker Haddock in the Evening We can only talk of Probabilities! BAR Some paths are more probable than others BAR I have always known that the electron is weird! REFERENCES 1. G. Gamov, Tompkins in Paperback, Canto Books. CUP, 1993 2. R.Gilmore, Alice in Quantum Land, Affiliated East West Press Ltd. 1994 3. Gribbin, Schrodinger’s Cat, Black Swan, London, 1984 4. Cropper, The Quantum Physicists, OUP, 1971 5. J. Gribbin, Schrodinger’s Kittens, Little, Brown & Co. London, 1995 6. G. Gamov and R. Stannard, The New World of Tompkins, Cambridge Univ. Press, 1999 7. R.P. Feynamn, QED, Princeton University Press, 1988 8. R.P. Feynman and A.R. Hibbs, Quantum Mechanics and Path Integrals, McGraw Hill, New York, 1965. See: www.colorado.edu/physics2000 I think it is safe to say that no one understands quantum mechanics. Richard Feynman The reason universities have students is so they can teach the professors, and Feynman was one of the best (students). John Wheeler What do you think of Quantum Mechanics? OR