* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download View Presentation
Social anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Eating disorder wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive behavioral therapy wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Broken windows theory wikipedia , lookup
Drug rehabilitation wikipedia , lookup
Munchausen by Internet wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Treatments for combat-related PTSD wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary approaches to depression wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral theories of depression wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of depression wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Externalizing disorders wikipedia , lookup
Major depressive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
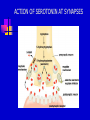
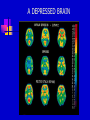
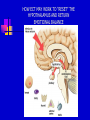
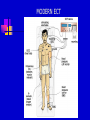
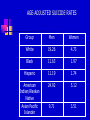
Chapter 10 Moods Disorders and Suicide TYPES OF MOOD DISORDER Depressive disorders Dysthymic disorder – Depressed mood most of the time Major depressive disorder – One or more major depressive episodes Bipolar disorders Cyclothymic disorder – Hypomanic episodes with depressive symptoms Bipolar I disorder – Manic and depressive episodes Bipolar II disorder – Major depressive episodes but without manic episodes Other mood disorders Mood disorder due to general medical condition Substance-induced mood disorder CAUSES AND TREATMENT OF DEPRESSION Interactional theory Interaction between biological characteristics, psychological vulnerabilities, and stressful life events or ongoing stressful life situations Biological theory Abnormality in serotonin, catecholamines, GABA, and acetylcholine HEREDITY RISK OF DEVEOPING A MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER ACTION OF SEROTONIN AT SYNAPSES A DEPRESSED BRAIN TREATMENT OF DEPRESSION Biological treatment Interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) Psychodynamic focus on relationships and social support in times of stress Behavioral treatment Antidepressant drugs Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) Social skills training Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) Change dysfunctional thought patterns and modify maladaptive behaviors HOW ECT MAY WORK TO “RESET” THE HYPOTHALAMUS AND RETURN EMOTIONAL BALANCE MODERN ECT CAUSES AND TREATMENT OF BIPOLAR DISORDER Cause Genetic vulnerability Environmental and family stress Treatment Lithium and anticonvulsant drugs Family psychoeducation and therapy MOOD COMBINATIONS FOUND IN BIPOLAR DISORDER Mania – Episodes of abnormally elevated, expansive or irritable mood Hypomania- Milder elevated state Depression – Diminished interest , energy, and ability to enjoy pleasure Mixed mania – Mania or hypomania occurs simultaneously with depressive symptoms Cyclothymia – Mood swings between hypomania and less severe depression Rapid cycling – Four or more episodes of depression, mania, or hypomania that are separated from each other by periods of relatively normal mood SUICIDE Mental illness and suicide Mental illness greatly increases probability of suicide attempt. Highest rate is for bipolar II disorder; lowest rate is for unipolar depression. Risk factors for Suicide Age – Teenagers, young adults, and people past middle age are highest risk. Sex – Men have higher completion rate. Race and ethnicity – American Indian and Alaskan Native groups have highest rates; white men the next highest. AGE-ADJUSTED SUICIDE RATES Group Men Women White 19.26 4.73 Black 11.63 1.97 Hispanic 11.19 1.74 American Indian/Alaskan Native Asian Pacific Islander 24.92 5.12 9.71 3.51 SUICIDE Themes for those with suicidal preoccupations Life events and suicide Stressful life events, especially involving loss, may be precipitating factors Suicide contagion Negative expectations and hopeless Perfectionism Well-known person’s suicide can increase Parasuicide – Suicidal behavior that does not result in death SUICIDE PREVENTION Increased awareness of suicidal thinking Provision of crisis centers Changing cultural expectations about dealing with the problem Postvention programs after suicide helps survivors MAJOR WARNING SIGNS OF SUICIDE IN ADOLESCENT BEHAVIOR Changes in eating and sleeping habits Withdrawal from family, friends, and regular activities Violent actions, rebellious behaviors, running away Drug and alcohol use Neglect of personal appearance Marked personality change Somatic complaints (headaches and stomach aches) Loss of interest in pleasurable activities Inability to tolerate praise or rewards