* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Social Psychology: Personal Perspectives (Chapter 14)
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar II disorder wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
History of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Postpartum depression wikipedia , lookup
Major depressive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral theories of depression wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
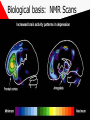
Psychological disorders (Chapter 16) Second Lecture Outline: Depression Personality Disorders Dissociative Identity Disorder Mood Disorders • Unipolar depression • 10-20% depressed at some point in life • multiple causes • low self-esteem, loss of motivation, pessimism • women > men • • • • Bipolar disorder 1% of population genetically mediated depressive and manic symptoms • mania related to high energy and shifts of attention Symptoms of depression Persistent sad, anxious, or "empty" mood Loss of interest or pleasure in activities Restlessness, irritability, crying Feelings of guilt, worthlessness, helplessness, hopelessness Sleeping disruption, early-morning awakening Appetite and/or weight loss or overeating and weight gain Decreased energy, fatigue, feeling "slowed down" Thoughts of death or suicide Difficulty concentrating, remembering, or making decisions Causes of Depression • Attachment explanations: Depression results from loss of a significant relationship • Behavioral: Learned helplessness due to uncontrollable punishment. Dogs. • Cognitive: Beck’s errors in thinking – – – – Arbitrary inference “They hate me.” Selective abstraction “Lawn has weeds” Stability “I am a failure” Lack of control: “Nothing I do will help my situation” Psychophysiology of Depression • Low levels of neurotransmitters are linked to depression • Drugs affect serotonin reuptake (SRIs) • Prozac • Mania treated with lithium carbonate: mood-leveling drug • Epinephrine decreased during depression -- hormonal factors Biological basis: NMR Scans Who were the lambs, Clarice? Personality Disorders • Stable & extreme personality features that affect happiness or adjustment • Examples: – – – – – Paranoid: suspicious of others Borderline: Mood and self-image unstable Narcissistic: Self-centred, no empathy Histrionic: Dramatic, manipulative, shallow Antisocial: Break law, cheat & lie, no concern for others, lack empathy, impulsive, brain involvement Dissociative Disorders • Dissociative amnesia: Memory loss for specific events or people • Fugue: Total memory loss after stress, relocation and starting a new life • Dissociative Identity Disorder (MPD) – two or more identities that coexist – associated with child trauma such as abuse – abused children “leave their bodies” – hearing voices