* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hormones
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
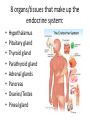
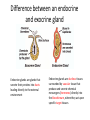
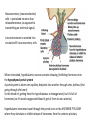
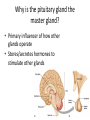
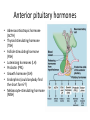
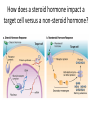
Endocrine System Answers 8 organs/tissues that make up the endocrine system: • • • • • • • • Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Thyroid gland Parathyroid gland Adrenal glands Pancreas Ovaries/Testes Pineal gland Difference between an endocrine and exocrine gland Endocrine glands are glands that secrete their proteins into ducts leading directly to the external environment Endocrine glands are ductless tissues surrounded by vascular tissue that produce and secrete chemical messengers (hormones) directly into the bloodstream, where they act upon specific target tissues What is a neurohormone? How does the hypothalamus control hormone release by the anterior pituitary gland? Neurosecretory (neuroendocrine) cells = specialized neurons that releasehormones (as opposed to transmitting an electrical signal) A neurohormone is secreted into circulation BY neurosecretory cells When stimulated, hypothalamic neurons secrete releasing /inhibiting hormones into the hypophyseal portal system A portal system is when one capillary bed pools into another through veins (without first going through the heart) So the blood it’s getting from the hypothalamus is deoxygenated, but it’s full of hormones (so if it needs oxygenated blood it gets it from its own arteries) Hypothalamic hormones travel through the portal veins to the ANTERIOR PITUITARY where they stimulate or inhibit release of hormones from the anterior pituitary Why is the pituitary gland the master gland? • Primary influencer of how other glands operate • Stores/secretes hormones to stimulate other glands What is the function of a hormone? • Hormones are specialized substances that coordinate the activities of specific target cells in certain areas of the body 3 ways by which a gland can be stimulated to release a particular hormone • In response to another hormone (e.g. GHRH from the hypothalamus will stimulate GH release from the pituitary) • By nerve impulses (e.g. nerve impulses can stimulate ACh release into the synaptic cleft) • Directly via internal changes (e.g. high blood sugar will cause the pancreas to release insulin) Anterior pituitary hormones • Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) • Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) • Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) • Luteinizing hormones (LH) • Prolactin (PRL) • Growth hormone (GH) • Endorphins (could anybody find the short form??) • Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) 2 hormones stored/released from the posterior pituitary. What stimulates their release? 1) Oxytocin 2) Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) Stimulated by the hypothalamus (during such times as increased plasma osmolality or infant suckling) How does a steroid hormone impact a target cell versus a non-steroid hormone?