* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Body Systems - Bishop Ireton High School
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hypoglycemia wikipedia , lookup
Diabetes in dogs wikipedia , lookup
Blood sugar level wikipedia , lookup
Artificial pancreas wikipedia , lookup
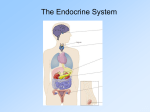
Endocrine Function Produce hormones-released into bloodstream Maintain homeostasis Works through negative feedback: Obtaining a desired response to a hormone inhibits further production or secretion of that hormone. Example- when blood glucose levels are high, insulin is produced to remove glucose from blood. Glucose is stored in the cells. When blood glucose levels are low, glucagon is produced to cause cells to release stored glucose into the blood. When desired level is reached, hormone production is turned off. Other example of negative feedback- when body doesn’t take in enough water it becomes dehydrated. Anti diuretic hormone(ADH) will be produced to tell large intesine to absorb as much water as possible. Hormone- substance produced in one area (like a gland) that has an effect in another area or target cell. Glands produce and release hormones into blood stream. 2 types of hormones Steroid-fat soluble- move through cell membrane easily Nonsteroid- need a receptor on cell membrane to bind to it. This sends signal inside cell that causes another enzyme to act as messenger to cause effect. Hypothalmus-in brain Master gland- controls nervous system and endocrine system. Will stimulate pituitary gland to release its own hormones to stimulate other glands. Pituitary Gland-in skull Pituitary Gland Hormone Action Posterior ADH Kidneys reabsorb water Posterior Oxytocin Uterine contactions and milk production Anterior FSH Production of egg and sperm LH Prepares uterus for implantation TSH Release thyroxin from thyroid GH Protien synthesis in cells Prolactin Milk production ACTH Stimulates adrenal cortex Thyroid Gland In base of the neckRegulates boby’s metabolism by production of thyroxine Too much- hyperthyroidism- weight loss, nervousness Too little- hypothyroidism- weight gain, lethargy Parathyroid Gland Located behind thyroid Parathyroid Hormone regulates calcium levels Adrenal Gland-Cortex Aldosterone- regulates Na reabsorption and excretion of K Pancreas Maintains blood glucose levels Insulin lowers BG. Glucagon increases BG.