* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cranial nerve ppt
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
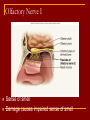
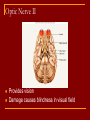
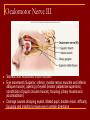
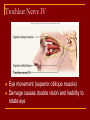
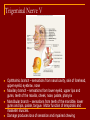
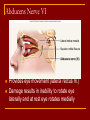
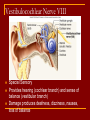
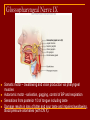
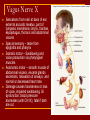
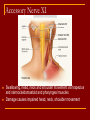
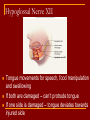
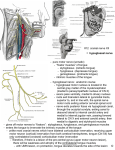
Cranial Nerves I through XII Olfactory Nerve I Sense of smell Damage causes impaired sense of smell Optic Nerve II Provides vision Damage causes blindness in visual field Oculomotor Nerve III Somatic and Autonomic motor function Eye movement (Superior, inferior, medial rectus muscles and inferior oblique muscle), opening of eyelid (levator palpebrae superioris), constriction of pupil (circular muscle), focusing (ciliary muscle and accomodation) Damage causes drooping eyelid, dilated pupil, double vision, difficulty focusing and inability to move eye in certain directions Trochlear Nerve IV Eye movement (superior oblique muscle) Damage causes double vision and inability to rotate eye Trigeminal Nerve V Ophthalmic branch – sensations from nasal cavity, skin of forehead, upper eyelid, eyebrow, nose Maxillary branch – sensations from lower eyelid, upper lips and gums, teeth of the maxilla, cheek, nose, palate, pharynx Mandibular branch – sensations from teeth of the mandible, lower gums and lips, palate, tongue. Motor function of temporalis and masseter muscles. Damage produces loss of sensation and impaired chewing Abducens Nerve VI Provides eye movement (lateral rectus m.) Damage results in inability to rotate eye laterally and at rest eye rotates medially Facial Nerve VII Somatic Motor - facial expressions Autonomic Motor - salivary and lacrimal glands, mucous membranes of nasal and palatine mucosa Special Sensory - taste on anterior 2/3’s of tongue Damage produces sagging facial muscles and disturbed sense of taste (no sweet and salty) Vestibulocochlear Nerve VIII Special Sensory Provides hearing (cochlear branch) and sense of balance (vestibular branch) Damage produces deafness, dizziness, nausea, loss of balance Glossopharyngeal Nerve IX Somatic motor – Swallowing and voice production via pharyngeal muscles Autonomic motor - salivation, gagging, control of BP and respiration Sensations from posterior 1/3 of tongue including taste Damage results in loss of bitter and sour taste and impaired swallowing, blood pressure anomalies (with CN X). Vagus Nerve X Sensations from skin at back of ear, external acoustic meatus, part of tympanic membrane, larynx, trachea, espophagus, thoracic and abdominal viscera Special sensory – taste from epiglottis and pharynx Somatic motor – Swallowing and voice production via pharyngeal muscles Autonomic motor – smooth muscle of abdominal viscera, visceral glands secretions, relaxation of airways, and normal or decreased heart rate. Damage causes hoarseness or loss of voice, impaired swallowing, GI dysfunction, blood pressure anomalies (with CN IX), fatal if both are cut Accessory Nerve XI Swallowing, head, neck and shoulder movement via trapezius and sternocleidomastoid and pharyngeal muscles Damage causes impaired head, neck, shoulder movement Hypoglossal Nerve XII Tongue movements for speech, food manipulation and swallowing If both are damaged – can’t protrude tongue If one side is damaged – tongue deviates towards injured side