* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10 - Brands Delmar
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Perceptual learning wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
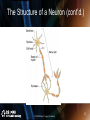
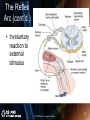
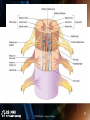
PowerPoint Presentation to Accompany © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 1 Chapter 10 The Nervous System Introduction, Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 2 Introduction • Control center and communication network – Directs functions of body’s organs and systems – Interprets external environment – Determines reaction to change © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 3 Introduction (cont’d.) • Homeostasis: balanced internal environment – Controlled by nervous and endocrine systems © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 4 Organization © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 5 Organization (cont’d.) • Central nervous system: brain and spinal cord • Peripheral nervous system – Afferent peripheral system • Sensory neurons – Efferent peripheral system • Somatic • Autonomic - sympathetic and parasympathetic © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 6 Organization (cont’d.) © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 7 Classification of Nerve Cells © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 8 Neuroglia Cells • Astrocytes: support, connection, blood brain barrier • Oligodendroglia: support, myelin sheath formation • Microglial: phagocytosis • Ependymal: line the ventricles of the brain • Schwann: myelin sheaths in peripheral nervous system © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 9 The Structure of a Neuron • Cell body • Dendrites: receptive areas • Axon: extension of cell body – Schwann cells – Nodes of Ranvier © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 10 The Structure of a Neuron (cont’d.) © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 11 The Structure of a Neuron (cont’d.) • Multipolar: several dendrites coming off cell body • Bipolar: one dendrite and one axon • Unipolar: one process extending from cell body © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 12 The Structure of a Neuron (cont’d.) • Receptors: detect environmental stimuli • Sensory: receive impulse from receptor site • Internuncial: transmit impulse for interpretation and processing • Motor: reaction to the stimulus © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 13 The Physiology of the Nerve Impulse © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 14 The Physiology of the Nerve Impulse (cont’d.) • Nerve cell fiber resting potential – Na+ concentration higher on outside – K+ concentration higher on inside – Negative charge on inside – Positive charge on outside © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 15 The Physiology of the Nerve Impulse (cont’d.) • Depolarization: Na+ rush inside cell • Repolarization: K+ rush out to restore balance • Depolarization: Repolarization moves in one direction • Myelinated vs. unmyelinated • All-or-none law © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 16 The Synaptic Transmission © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 17 The Synaptic Transmission (cont’d.) • Synapse: axon terminal branches close to next dendrites • Impulse reaches axon terminals • Triggers neurotransmitter release into synaptic cleft © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 18 The Synaptic Transmission (cont’d.) • Neurotransmitters – Acetylcholine • Most common – Epinephrine – Norepinephrine – Serotonin – Dopamine – Endorphins © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 19 Animation – Firing of Neurotransmitters • This animation illustrates the physiology of the nerve impulse • [Insert FiringofNeurotransmitters.swf] © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 20 The Reflex Arc © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 21 The Reflex Arc (cont’d.) • Knee-jerk reflex • Maintain homeostasis – Heartbeat/breathing rates – Digestion – Coughing – Sneezing – Swallowing – Vomiting © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 22 The Reflex Arc (cont’d.) • Involuntary reaction to external stimulus © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 23 Grouping of Neural Tissue © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 24 Grouping of Neural Tissue (cont’d.) • White matter – Groups of myelinated axons – Forms nerve tracts in CNS • Gray matter – Nerve cell bodies and dendrites – Unmyelinated axon bundles – Cortex: gray matter on surface of brain © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 25 Grouping of Neural Tissue (cont’d.) • • • • Nerve: bundle of fibers outside CNS Ganglia: nerve cell bodies outside CNS Tract: bundle of fibers inside CNS Nucleus: nerve cell bodies and dendrites inside CNS • Horns: areas of gray matter in spinal cord © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 26 The Spinal Cord © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 27 Introduction • Continuation of medulla oblongata • 31 segments each with pair of spinal nerves • Protected by meninges – Dura mater – Arachnoid – Pia mater © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 28 © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 29 29 Functions of the Spinal Cord • Conveys sensory impulses to the brain • Integrates reflexes • Spinal nerves connect at roots – Dorsal root: sensory – Ventral root: motor © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 30 The Spinal Nerves © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 31 The Spinal Nerves (cont’d.) • All 31 pairs arise from union of dorsal and ventral roots • Mixed nerves consisting of motor and sensory fibers • Most exit vertebral column between vertebrae © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 32 The Spinal Nerves (cont’d.) • Named and numbered according to region and level of spinal cord – Cervical: 8 pairs – Thoracic: 12 pairs – Lumbar: 5 pairs – Sacral: 5 pairs – Coccygeal: 1 pair © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 33 Summary • Named the major division of the nervous system • Classified neurons and neuroglial cells • Discussed the physiology of the nerve impulse and transmission at synapses • Named the different types of neural tissue • Discussed the structure of the spinal cord • Named the spinal nerves © 2010 Delmar, Cengage Learning 34