* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SMELL & TASTE
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Sensory cue wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
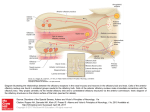
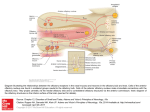
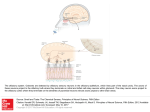
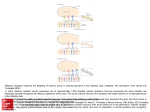
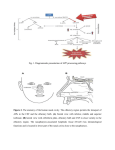
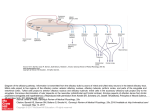
Olefaction Anthony J Greene 1 Smell • Chemical detection without the danger of ingesting poison • Object identification • Sexual signaling Anthony J Greene 2 Nasal Anatomy Anthony J Greene 3 Nasal Anatomy • Nasal cavity - Hollow portion of head behind nose warms air, filters out dust, houses the sense of smell • Olfactory epithelium - Area of nasal cavity with olfactory receptors Anthony J Greene 4 Nasal Anatomy • Receptors are genuine neurons (unlike photoreceptors and hair cells) • Unlike other neurons, receptors are continually regenerated • 1,000 different receptor types - about 1% of your DNA codes for olfactory receptors making it the largest single gene family Anthony J Greene 5 Olfactory Epithelium • Receptors have four parts cilia, olfactory knob, olfactory rod and the axon • Olfactory nerve - the axons of the olfactory receptors form bands which travel to the olfactory bulb Anthony J Greene 6 Olfactory Bulb • Olfactory bulb - organ which houses all the nerves which receive inputs from the olfactory receptors (mitral cells and periglomerular cells) • Limbic and Thalamic connections • Olfactory cortex (frontal lobe) 7 Early Olfactory Pathway Anthony J Greene 8 Central Olfactory Pathways Olefactory Cortex Limbic System Thalamus Olfactory Bulb Olfactory Receptors Odorant Anthony J Greene 9 Central Olfactory Pathways Olefactory Cortex Limbic System Thalamus Olfactory Bulb Olfactory Receptors Odorant Anthony J Greene 10 Central Olefactory Pathways Olefactory Cortex Limbic System Thalamus Olfactory Bulb Olfactory Receptors Odorant Anthony J Greene 11 Central Olefactory Pathways Olefactory Cortex Limbic System Thalamus Olfactory Bulb Olfactory Receptors Odorant Anthony J Greene 12 Central Olefactory Pathways Olefactory Cortex Limbic System Thalamus Olfactory Bulb Olfactory Receptors Odorant Anthony J Greene 13 Central Olefactory Pathways Olefactory Cortex Limbic System Thalamus Olfactory Bulb Olfactory Receptors Odorant Anthony J Greene 14 Perception of Smell • The dimensions of smell Foul Flowery Fruity Burnt Resinous Spicy Anthony J Greene 15 Perception of Smell (cont.) • We can distinguish between about 10,000 different smells Different threshold levels for different smells • Two thresholds for each smell -low threshold for the existence of a chemical, somewhat higher threshold to discriminate one smell from another Anthony J Greene 16 Perception of Smell (cont.) • Adaptation - Olfactory fatigue - cross-adaptation • Smell Constancy - receptors are more stimulated during a deep sniff than a shallow one - the judgment of odor intensity does not change - Anthony J Greene 17 Perception of Smell (cont.) Anthony J Greene 18 Pheromones: Mammals Powerful effects on behavior, specifically sexual behavior, territorial behavior and identification of kin Mammals • Most mammals only become sexually aroused in the presence of pheromones • Increased likelihood of pregnancy • Synchronization of estrus cycles • Mutual recognition of mother and offspring • Territory marking (e.g. dogs) 19 Pheromones: Mammals • Releasers - trigger a specific behavioral response • Primers - trigger a hormone response which increases the likelihood of certain types of behaviors Anthony J Greene 20 Pheromones: Humans Humans • infants can correctly identify their own mother's milk and are much more likely to nurse when its their own mother • female menstrual cycles can be altered by pheromones - the sorority effect • male and female behavior is highly influenced by pheromones t-shirt experiment - musky versus sweet • the musky odor is rated by males and females as unpleasant and is thought to serve as a territorial 21 marker among males Pheromones: Alpha Androstenol alpha androstenol (predominantly secreted by females) 1. Increase sexual arousal in males 2. Increases male perception of female attractiveness • women in photographs were rated as significantly more sexually attractive when judges were first exposed to alpha androstenol 3. Increases willingness of females to initiate social contact with males • females exposed to alpha androstenol were much more receptive to male-initiated contact • more likely to seek out male company • less likely to seek female company Anthony J Greene 22