* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download OPIOID ANALGESICS
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
Dextropropoxyphene wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
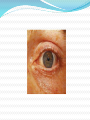
DR.SOBAN SADIQ OPIOID AGONISTS Morphine(strong mu receptor agonist) Codeine Heroin Pholcodine Meperidine(pethidine) Loperamide(over the counter for diarrhea) Diphenoxylate Dextromethorphan Opioid agonist-antagonist/partial agonist Nalbuphine Pentazocine Opioid antagonists Nalorphine Naloxone Naltrexone Opioid receptors Mu Kappa Delta MOA OF MORPHINE Certain opioid receptors are located on primary afferent and spinal cord pain transmission neurons(ascending pathways) and on neurons in the midbrain and medulla(descending pathways) that function in pain modulation. All 3 receptors appear to be involved in anti nociceptive and analgesics mechanisms. Presynaptically: Opioid receptor activation can close voltage – gated calcium ion channels to inhibit neurotransmitter release. ( serotonin, glutamate and substance P) Postsynaptically: Activation of these receptors can open potassium ion channels to cause membrane hyperpolarization(inhibitory post synaptic potential). -Direct inhibition of neurons in ascending pathways. Pharmacological effects CNS: Analgesia: most powerful drug available for relief of pain Euphoria: addict experiences a pleasant floating sensation and freedom from anxiety and distress. Sedation Respiratory depression: Main cause of death from opioid overdose due to reduced responsiveness of respiratory centre in brainstem to blood levels of CO2. Increase arterial CO2 retention causes cerebral vasodilation resulting in increase intracranial pressure Cough suppression: suppression of cough centre in nucleus of tractus solitarius Miosis: results from stimulation of Edinger- Westphal nucleus causing pin-point pupils except meperidine. Emesis: due to stimulation of brainstem chemoreceptor trigger zone results in nause and vomiting CVS: No significant direct effect on CVS Hypotension may occur if CVS is already stressed. Due to the peripheral arterial and venous dilation resulting from histamine release. GIT: Decrease intestinal propulsive peristalsis and stomach motility leads to constipation Biliary tract:Constriction of biliary smooth muscles leads to biliary colic except meperidine Constriction of sphincter of oddi leads to increase biliary pressure,reflux of biliary and pancreatic secretions and elevated plasma and lipase levels Renal functions: depressed due to decrease renal plasma flow. Also has antidiuretic effect.Mechanism involve both CNS and peripheral site Ureteral and bladder tone is increased Increased sphincter tone….urinary retention Occasionally, ureteral colic caused by renal calculus is made worse by opioid induced increase in ureteral tone Uterus: decrease uterine tone lead to prolong labor Skin: flushing and warming ,sweating,itching due to histamine release Summary Biliary, bladder,ureter tone inc. except meperidine (which block M receptors) GIT,uterine tone dec. Clinical uses Analgesia for Cough Diarrhea MI, terminal illness, surgery, obstetrical procedures, cancer. Acute pulmonary edema: decrease dyspnea Proposed mechanism : Reduced anxiety(perception of shortness of breath) Reduced cardiac preload(reduced venous tone) Reduced afterload(decreased peripheral resistance) If respiratory depression is there then use furosemide Adverse effects Tolerance Tolerance occur due to receptor uncoupling. Physical dependence: It results in withdrawal(Abstinence) syndrome if there is failure to continue administer drug. Sudden withdrawal(abstinence syndrome)has following signs/symptoms: lacrimation,yawning,chills,hyperventilation,hyperther mia,diarrhea,vomiting,anxiety Psychological dependence: euphoria, Indifference to stimuli and Sedation Morphine poisoning….antidote is naloxone 1-A 57 year old man presented with steady, severe pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, vomiting and temperature of 102 F. If hepatobiliary imaging reveals an obstructed cystic duct, which of the following agents would be the drug of choice for the treatment of this patient’s pain? a-Meperidine b-Morphine c-Naproxen d-Diphenoxylate e-Loperamide Fentanyl patches(opioid) have been used to provide analgesia. The most dangerous adverse effect of this mode of administration is a-Cutaneous reactions b- Diarrhea c- Hypertension d- Relaxation of skeletal muscle e- Respiratory depression Mr. Naseem is on his way to take an examination and he suddenly gets an episode of diarrhea. He stops at a nearby drug store for an over the counter opioid with anti diarrheal action, what would be his choice: a-Codeine b-Dextromethorphan c-Diphenoxylate d-Loperamide e-Nalbuphine Which of the following opioid analgesics is a strong mu receptor agonist? a- Naloxone b- Morphine c-Nalbuphine d- Hydrocodone e-Naltrexone Morphine causes the following effects EXCEPT: a) Constipation b) Dilatation of the biliary duct c) Urinary retention d) Respiratory depression The antidote of choice for morphine poisoning is A-Naltrexone B-Naloxone C-Nalbuphine D-Codeine Which of the following opioid analgesic is used for relieving the acute, severe pain of renal colic: a-Morphine b- Naloxone c- Codeine d- Meperidine e-Naltrexone Opioid acts presynaptically by blocking Sodium channels Potassium channels Calcium channels Serotonin channels GABA channels