* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EvolutionofPopulations209
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
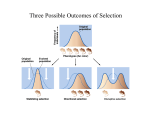
Industrial Melanism and Microevolution Hierarchical Classification Gene Flow additions to and/or subtractions from a population resulting in the movement of fertile individuals or gametes Gene Flow and Human Evolution Increasing migration of people throughout the world has contributed to an increase in gene flow Mutation and Sexual Recombination produce the variation that makes evolution possible Genetic Drift occurs by chance when only certain members of a population reproduce and pass on their genes Genetic Drift Bottleneck Effect: a sudden change in the environment drastically reduces the size of the population Cheetah Northern Elephant Seals Polydactylism in the Amish Population Founder Effect: migration of a small subgroup of the population Founder Effect in Amish Ellis-van Creveld Syndrome Causes dwarfism and polydactyly The evolution of fruit fly (Drosophila) species on the Hawaiian archipelago (Founder Effect) • Natural Selection is the primary mechanism of adaptive evolution • Out of all the factors that can affect a gene pool only natural selection is likely to adapt a population to its environment Mapping Malaria and the Sickle-Cell Allele This is a good example of heterozygote advantage. Modes of Selection Types of Selection • Most traits are polygenic - variations in the trait result in a bell-shaped curve • Three types of selection occur: 1) Directional Selection – the curve shifts in one direction ex: resistance to antibiotics by bacteria Directional Selection Evolution of the Horse over 50 million yrs Hyracotherium American Museum of Natural History Orohippus Note the toes! Directional selection for beak size in a Galápagos population of the medium ground finch Types of Selection –(2) Stabilizing Selection •Ex - when human babies with low or high birth weight are less likely to survive Stabilizing Selection Cepaea Disruptive Selection Snails (3) Disruptive Selection The curve has two peaks; dark shells appear in most forested areas whereas light-banded shells appear in areas of low lying vegetation Ex – When Cepaea snails vary because a wide geographic range causes selection to vary Disruptive or Diversifying Selection Small-billed birds feed on soft seeds; largebilled birds feed on hard seeds (Blackbellied Seed Crackers – Cameroon, Africa) The Two-Fold Disadvantage of Sex Why Natural Selection Cannot Fashion Perfect Organisms 1) Evolution is limited by historical constraints. 2) Adaptations are often compromises. 3) Chance and natural selection interact. 4) Selection can only edit existing variations. Natural selection can affect the distribution of phenotypes in three ways. They are: _______________ selection _______________ selection and _______________ selection. A small population of organisms is suddenly cut off from the others in the population. This is known as the _____________ effect. A small group of organisms migrates from one area to another. There is not a wide variation in the gene pool. This is known as the ___________ effect.