* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diseases and the Human Body Rubella Infectious
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Bioterrorism wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Yellow fever in Buenos Aires wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
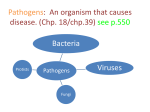
Diseases and the Human Body Rubella 1) Infectious illness with flu-like symptoms followed by a rash. 2) Caused by a virus 3) Low-grade fever, Headache, runny nose red eyes, Muscle or joint pain 4) Body systems affected - Respiratory (running nose), integumentary (rash on skin), muscular, skeletal Pertussis 1) Infectious - aka Whooping cough, is an infectious bacterial disease that causes uncontrollable coughing 2) Caused by bacteria 3) You may have choking spells or may cough so hard that you vomit 4) Body systems affected - Respiratory system, lungs These are three images of children with Pertussis. The child on the left has broken blood vessels in the eyes and bruising on face due to pertussis coughing. Salmonellosis (salmonella) 1) Infectious – from contaminated food 2) Caused by bacteria, no vaccine available 3) diarrhea, fever, and abdominal cramps 4) Body systems and/or organs affected – digestive system, stomach, intestines Yellow Fever 1) Infectious virus, transmitted to humans through the bite of infected mosquitoes 2) Caused by a virus 3) Symptoms - fever and chills, severe headache, back pain, general muscle aches, nausea, fatigue, and weakness. Affects the LIVER-causes Jaundice 4) Body systems – muscular system, nervous system Bubonic Plague 1) Infectious - bacteria are found mainly in rats and in the fleas that feed on them. People and other animals can get plague from rat or flea bites. In the 1300s, the "Black Death," as it was called, killed approximately one-third of Europe's population. Today plague is uncommon. This is largely due to better living conditions and antibiotics. 2) Caused by bacteria 3) Chills, high fever, muscle pain, severe headache, seizures 4) Body systems – respiratory, muscular Dengue Fever 1) Infectious - virus transmitted by mosquitoes 2) Caused by a virus 3) Severe headache, joint pain, muscle and/or bone pain, rash, bleeding, low white cell count 4) Body systems – skeletal, muscular, integumentary, circulatory Strep Throat 1) Infectious – passed from person to person 2) Caused by bacteria often found in the throat and on the skin 3) Symptoms - severe pain and swelling in the throat, fever 4) Body systems – respiratory, throat Mononucleosis 1) Infectious - one of the most common human viruses 2) Caused by a virus and requires intimate contact with the saliva (found in the mouth) of an infected person. 3) Symptoms - fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph glands 4) Body systems – respiratory system, lymphatic system, circulatory system Ringworm 1) Infectious 2) Caused by a fungus, “ringworm” is not caused by a worm, but rather by a type of fungus called a “dermatophyte.” Spread usually occurs through direct contact with an infected person or animal. Clothing, bedding and towels can also become contaminated and spread the infection. 3) Symptoms – itchy skin on almost any area of the body, such as the scalp, legs, arms, feet and groin. Redness, scaling, or fissuring of the skin, or a ring with irregular borders and a cleared central area may occur. 4) Body systems - integumentary Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease 1) Noninfectious, a very rare genetic mutation 2) Causes - unknown spontaneous genetic mutation 3) Symptoms - Personality changes, anxiety depression , memory loss, impaired thinking, blurred vision, insomnia 4) Body systems – nervous system, a degenerative brain disorder that leads to dementia and, ultimately, death. Symptoms of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) sometimes resemble those of other dementia-like brain disorders, such as Alzheimer's. Diseases and the Human Body Parkinson’s Disease • 1). Non infectious –No Cure • 2.) Cause of the disease is unknown but genetics and environment are factors. • 3.) Symptoms include tremors in the hands, as the disease progress, it affects the brain; slow movement, stiffness in muscles and balance and coordination • 4.) Brain-Nervous System Small Pox • 1.) Infectious- person to person contact • 2.) Cause- Virus • 3.) Symptoms- Flu-like: fever, headache, rash • 4.) Replicates itself in the blood vesselscirculatory system. Skin- Integmentary system Lyme Disease • 1.) Infectious- Deer Tick bite • 2.) Cause – Bacteria • 3.) Symptoms- Flu-Like; fever, headache, fatigue and rash. If left untreated, could affect the joints, heart and brain. • 4.) Integmentary, Skeletal, Circulatory and Nervous Systems Skin Cancer • 1.) Non infectious- an abnormal growth of skin cells • 2.) Caused by exposure to the SUN • 3.) Symptoms- freckles, moles and small lesions that change shape and color. • 4.) All skin tones can be affectedIntegmentary system Mumps • 1.) Infectious- vaccine available • 2.) Cause- Virus • 3.) Symptoms- Flu-like; fever, headache, muscle pain, tired and weakness followed by swollen salivary glands. • 4.) Muscle and Skeletal systems Anthrax • 1.) Infectious- Bacterial Disease • 2.) 3 Types: Skin- sore turns to blister which turns to ulcer. Treated w/ antibotics • Digestive-nausea, not eating, bloody diarrhea, fever and stomach pain. 1/3 people die from this type • Breathing anthrax- Lungs-Flu like systems With sore throat. ½ people die from this type Asthma • 1.) Non infectious • 2.) Symptoms- wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness and early morning and night time coughing. • 3.) Lungs-Respiratory System HIV/AIDS • 1.) Human Immunodeficiency Virus leads to Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome • Infectious spread through unprotected sexual transmission and blood to blood contact. • Symptoms- may not show up for up to 10 years after being affected w/ the virus. However, the virus continues attacking and destroying the Immune System, until the body cannot fight off other diseases and cancers. Symptoms • • • • • • • • • Swollen lymph nodes Fever – nervous system Diarrhea - digestive system Headache Muscle aches – muscular system Nausea and vomiting - digestive Rash on the abdomen, arms and legs and face Sore throat – integmentuary system Thrush, a fungal infection of the mouth • The HIV virus was first diagnosed in West Africa. Humans who hunted chimpanzee’s for their meat came in contact with infected chimps blood. • HIV was first recognized in the United States in 1981 • Kaposi Sarcoma Diphtheria • Infectious- children under 5 and adults over 60. • Cause-Bacterial • Symptoms- begin w/ fever, sore throat, swollen neck glands. Can progress to; a thick gray/black fuzz that affects the nose, throats and may block the air way Affects- respiratory, digestive systems