* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Scarlet fever
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis signs and symptoms wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
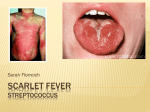
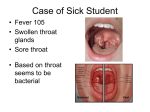
Scarlet fever (Streptococcus pyogenes) This is a bacterial infection caused by the same bacteria as ‘strep throat’. It is also known as scarlatina. Symptoms: Fever, sore throat, ‘strawberry tongue’ (swollen, red spots enlarged), characteristic rash which appears 12-48 hours after the fever. The rash is fine and has a sandpaper like feel. It generally starts on the chest and spreads. In skin folds it has a classic red streak effect. The rash will blanch (turn white) when pressed. By the 6th day of infection the rash will start fade and the skin will peel. Peeling may last up to 10 days. Other symptoms may be abdominal pain, vomiting, head ache and muscle/joint pain. Transmission: The time between becoming infected and presenting of symptoms is short, 1-2 days. Infection occurs by contact with the infected person’s respiratory secretions through the air when that person coughs or sneezes or skin contact with infected secretions which are then transferred to the eyes /nose/mouth. Sharing eating utensils or cups is also a means of transmission. Good hand washing and general hygiene practices essential to prevent its spread. Children should blow their noses frequently and wash hands afterwards to prevent shared surfaces like tables being contaminated with mucus. When the appropriate treatment has commenced, the child is no longer contagious after 24hours of taking it. Thorough cleaning of all surfaces and disinfection of cups and eating utensils is advisable. Treatment: The treatment of scarlet fever is like that of strep throat, antibiotics that are effective against that particular bacteria. These should be taken exactly as directed until finished and stored correctly. As with other fever inducing illnesses, paracetemol must be given to lower the temperature and for pain relief. Gargling with salt water or antiseptic solutions may help the throat.