* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Strep
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Ankylosing spondylitis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
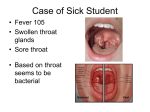
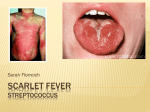
Date_____________________ Dear Parent: Streptococcal disease has been reported in your child’s classroom. Identification: Streptococcal disease (group A-Beta Hemolytic) often called "strep" cause a wide variety of infections. The most common is sore throat or skin infections (impetigo). Other diseases such as scarlet fever, middle ear infections and pneumonia can be caused by the strep bacteria. Patients with strep have sore throat, fever, spots on the tonsils and back of throat, and swollen lymph nodes. Severe problems resulting from strep can be rheumatic fever and kidney disease (glomerulonephritis) which occurs days to weeks after a strep infection. Strep can also cause scarlet fever. Symptoms of Scarlet Fever: A fine, bright red rash, a flushed face with a white ring around mouth, and a coated tongue with "strawberry" appearance can occur. The disease usually begins 1-3 days after exposure. Treatment: Streptococcal disease (group A-Beta Hemolytic) is usually treated with penicillin for ten days. Treatment is important to prevent complications. Methods of Control: 1. Keep sick children home. The exclusion may be terminated 24 hours after adequate treatment is begun if therapy is continued for 10 days. The child's doctor decides when the child can return to school. 2. Cover coughs and sneezes with disposable tissues. Wash hands often. 3. If your child has been exposed to streptococcal disease and he/she develops symptoms, see your doctor for his advice and care. Call your doctor, or Maricopa County Health Department (602-506-6767) if you have questions.