* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download seismic waves
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Seismic inversion wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Seismic communication wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Surface wave inversion wikipedia , lookup
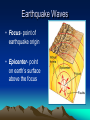
EARTHQUAKES!!! Earthquakes • Earthquake: Sudden movement of rock sliding along a fault in the earth’s crust • Releases energy as this occurs. • Energy release produces strong vibrations called seismic waves. Energy Release • Edges of the plates get stuck while the rest of the plate keeps moving.—Energy stored up • When the force of the moving blocks finally overcomes the friction of the jagged edges of the fault and it unsticks, all that stored up energy is released. • The energy radiates outward from the fault in all directions in the form of seismic waves like ripples on a pond. –This is the earthquake Earthquake Waves • Focus- point of earthquake origin • Epicenter- point on earth’s surface above the focus • Primary Waves ( P-wave) – Travel through solids and liquids – Travel FAST! • Secondary Waves (S-waves) – Only travel through solids – Travel SLOWER than P-waves Longitudinal Waves (L-waves) -- Travel on earth’s surface http://losangeles.cbslocal.com 3/17 la eq http://earthguide.ucsd.edu/mystery_detectives/teach/epi center/ia_graph_travel_time_animation.html Mystery Earthquake animations: http://earthguide.ucsd.edu/mystery_detectives/teach/epi center/show.html TO know the EPICENTER:(where quake started) • Seismic waves radiate out from the source in all directions. • Siesmograph stations recieve p and s waves and use the difference in arrival time to determine the distance away. • Different stations compare the information recorded at the same time. Seismic Station picks up p and s waves and determines they came from an earthquake 10 km away. But 10 km from which direction? A second seismic station records the same quake at 5 km away. This narrows down the epicenter to 2 spots. To pinpoint the epicenter, 3 seismic stations must record the quake. (triangulation) VOLCANOES • A hole in Earth’s crust through which lava flows from underground. Origin of Magma • Molten rises from the Earth’s asthenosphere (upper mantle) to the Earth’s surface through cracks creating a volcano. Most volcanoes occur along plate boundaries Hot Spots • Volcanically active sites that arise in places where large quantities of magma move to the surface in large, column-like plumes – Can occur away from plate boundary – When under a oceanic plate, volcanic island chains forms • Mountains—folding and faulting; convergent continental boundaries • Plateau– eroded mountain