* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake engineering wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
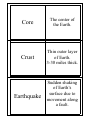
Geology Flash Cards Grade 3 January 2015 Core Crust Earthquake Epicenter Fault Hazard Latitude Longitude Magnitude Mantle Richter scale Ring of Fire Seismic Waves Seismogram Tectonic plates Tsunami Volcano Waves Core The center of the Earth. Crust Thin outer layer of Earth. 3-30 miles thick. Earthquake Sudden shaking of Earth’s surface due to movement along a fault. Epicenter Place on ground directly above an earthquake. Fault Break in Earth’s crust. Boundary between two plates. Hazard A dangerous situation. Latitude Distance measured north or south from the Equator. Longitude Distance measured east or west from Prime Meridian. Magnitude The measure of the size of an object or event. Mantle Earth’s layer between the core and crust. Richter Scale A scale that measures earthquake strength. Ring Of Fire Location of most earthquakes and volcanoes. Seismic Waves Energy waves produced by an earthquake. Seismogram Records seismic waves made by an earthquake. Tectonic Plates Pieces of Earth’s crust that “float” on mantle layer. Tsunami A large water wave, or group of waves, caused by an earthquake. Volcano Mountain formed by rise of molten rock from inside the Earth. Waves Transfer of energy with a repeating pattern.