SG Chapters 2 and 3 Answer Section
... a. east and west of the prime meridian. c. north and south of the prime meridian. b. east and west of the equator. d. north and south of the equator. ____ 62. Longitude indicates positions using a. parallel circles east and west of the prime meridian. b. semicircles east and west of the prime meridi ...
... a. east and west of the prime meridian. c. north and south of the prime meridian. b. east and west of the equator. d. north and south of the equator. ____ 62. Longitude indicates positions using a. parallel circles east and west of the prime meridian. b. semicircles east and west of the prime meridi ...
Chapter 6. The Shape of the Earth
... erosion and lower crustal delamination, are associated with low relief, less than 1 km, and thinner crusts. Regional changes in the topography of the continents are generally accompanied by changes in mean crustal thickness . Continents stand high because of thick, low-density crust, compared with o ...
... erosion and lower crustal delamination, are associated with low relief, less than 1 km, and thinner crusts. Regional changes in the topography of the continents are generally accompanied by changes in mean crustal thickness . Continents stand high because of thick, low-density crust, compared with o ...
Practicing Map Skills
... Using the scale bar to measure distances between places on a map is easy. Use a piece of paper. Put the edge of the paper between the two points you wish to measure. Make a mark on the paper at each point. Then put the piece of paper on the scale bar with one mark at zero. Note where the other point ...
... Using the scale bar to measure distances between places on a map is easy. Use a piece of paper. Put the edge of the paper between the two points you wish to measure. Make a mark on the paper at each point. Then put the piece of paper on the scale bar with one mark at zero. Note where the other point ...
Cadet Core Textbook 3 - Spruce Creek High School
... Pole to the South Pole and are equal in length. The imaginary horizontal lines on the globe are the latitude or parallel lines. These lines are parallel to each other and form complete circles around the globe. The horizontal lines of latitude and the vertical lines of longitude are further broken d ...
... Pole to the South Pole and are equal in length. The imaginary horizontal lines on the globe are the latitude or parallel lines. These lines are parallel to each other and form complete circles around the globe. The horizontal lines of latitude and the vertical lines of longitude are further broken d ...
Table Valued Functions: The Key Idea
... (http://skyserver.sdss.org/) for the astronomy community. The SkyServer is a multiterabyte database that catalogs about 300 million celestial objects. Many of the questions astronomers want to ask of it involve spatial searches. Typical queries include, “What is near this point?” “What objects are i ...
... (http://skyserver.sdss.org/) for the astronomy community. The SkyServer is a multiterabyte database that catalogs about 300 million celestial objects. Many of the questions astronomers want to ask of it involve spatial searches. Typical queries include, “What is near this point?” “What objects are i ...
FREE Sample Here
... B) the first "true" maps appeared because of modern printing presses in the 20th century. C) sailors during the European Renaissance had paper maps that were far more useful to them than were the "stick charts" possessed by Polynesian sailors and fishers. D) maps have appeared in many forms in diffe ...
... B) the first "true" maps appeared because of modern printing presses in the 20th century. C) sailors during the European Renaissance had paper maps that were far more useful to them than were the "stick charts" possessed by Polynesian sailors and fishers. D) maps have appeared in many forms in diffe ...
Preview Sample File
... Learning Outcome: 1. 5: Identify contemporary analytic tools, including remote sensing, GPS, and GIS Global Sci L.O.: 2. Demonstrate the ability to think critically and employ critical thinking skills 29) A geographer might use a GPS to A) log the locations where photographs were taken, but not to f ...
... Learning Outcome: 1. 5: Identify contemporary analytic tools, including remote sensing, GPS, and GIS Global Sci L.O.: 2. Demonstrate the ability to think critically and employ critical thinking skills 29) A geographer might use a GPS to A) log the locations where photographs were taken, but not to f ...
FREE Sample Here
... 12) We can judge from the various kinds of maps shown in this chapter that A) fairly accurate navigational maps could only be produced after the start of the Industrial Revolution. B) the first "true" maps appeared because of modern printing presses in the 20th century. C) sailors during the Europea ...
... 12) We can judge from the various kinds of maps shown in this chapter that A) fairly accurate navigational maps could only be produced after the start of the Industrial Revolution. B) the first "true" maps appeared because of modern printing presses in the 20th century. C) sailors during the Europea ...
A Comparison of Equatorial Electrojet in Peru and East Brazil
... along the geographic meridian, and at Itinga (ITI, 4.3oS, 47.0oW, inclination 1.4oN, declination 19.3oW) in eastern part of South America, where the geomagnetic field is aligned about 19o west of the geographic meridian; although the mean intensity of the magnetic field in the two regions are almost ...
... along the geographic meridian, and at Itinga (ITI, 4.3oS, 47.0oW, inclination 1.4oN, declination 19.3oW) in eastern part of South America, where the geomagnetic field is aligned about 19o west of the geographic meridian; although the mean intensity of the magnetic field in the two regions are almost ...
Draft 2.5 - posted 15 June 2014 /2500k
... On this graph, one-tenth second (0".10) of geocentric arc equals 3.0818 meters on Earth's surface near the North Pole. Decades are marked and labeled to show the nonuniform nature of drift speed. It is apparent that when drift direction is changing more rapidly, the pole drifts more slowly. Although ...
... On this graph, one-tenth second (0".10) of geocentric arc equals 3.0818 meters on Earth's surface near the North Pole. Decades are marked and labeled to show the nonuniform nature of drift speed. It is apparent that when drift direction is changing more rapidly, the pole drifts more slowly. Although ...
FREE Sample Here
... Full file at http://testbankeasy.eu/Test-bank-for-The-Cultural-Landscape,-9th-Edition---J ames-M.-Rubenstein 16) A ship's position is given as 0 degrees latitude and 27 degrees west longitude. We can conclude from this information that the ship is located A) on the equator. B) at the North or South ...
... Full file at http://testbankeasy.eu/Test-bank-for-The-Cultural-Landscape,-9th-Edition---J ames-M.-Rubenstein 16) A ship's position is given as 0 degrees latitude and 27 degrees west longitude. We can conclude from this information that the ship is located A) on the equator. B) at the North or South ...
FREE Sample Here
... http://testbanksexpress.eu/test-bank-for-the-cultural-landscape-9th-edition-james-m-rubenstein.ht ml 16) A ship's position is given as 0 degrees latitude and 27 degrees west longitude. We can conclude from this information that the ship is located A) on the equator. B) at the North or South Pole. C) ...
... http://testbanksexpress.eu/test-bank-for-the-cultural-landscape-9th-edition-james-m-rubenstein.ht ml 16) A ship's position is given as 0 degrees latitude and 27 degrees west longitude. We can conclude from this information that the ship is located A) on the equator. B) at the North or South Pole. C) ...
The Cultural Landscape: Introduction to Human Geography, 9e
... http://testbanksolution.eu/Test-Bank-Bank-for-The-Cultural-Landscape-An-Introduction-To-Hu man-Geography-9-E-by-Rubenstein 16) A ship's position is given as 0 degrees latitude and 27 degrees west longitude. We can conclude from this information that the ship is located A) on the equator. B) at the N ...
... http://testbanksolution.eu/Test-Bank-Bank-for-The-Cultural-Landscape-An-Introduction-To-Hu man-Geography-9-E-by-Rubenstein 16) A ship's position is given as 0 degrees latitude and 27 degrees west longitude. We can conclude from this information that the ship is located A) on the equator. B) at the N ...
Sample
... C) Every parallel begins and ends at the poles. D) Every parallel is the same length. E) Every meridian is distorted by magnetic declination. Answer: B Diff: 2 ...
... C) Every parallel begins and ends at the poles. D) Every parallel is the same length. E) Every meridian is distorted by magnetic declination. Answer: B Diff: 2 ...
The Cultural Landscape: Introduction to Human Geography Thinking
... C) Every parallel begins and ends at the poles. D) Every parallel is the same length. E) Every meridian is distorted by magnetic declination. Answer: B Diff: 2 ...
... C) Every parallel begins and ends at the poles. D) Every parallel is the same length. E) Every meridian is distorted by magnetic declination. Answer: B Diff: 2 ...
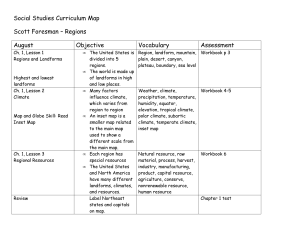
Social Studies Curriculum Map Scott Foresman – Regions August
... A timeline is a tool used to organize ...
... A timeline is a tool used to organize ...
Look at a political map of the United States.
... world map. Suppose it is your job to send out rescue crews to save ships when they are in trouble. One day you receive a notice from a ship’s captain. He informs you that his location is approximately 20oS latitude and 80oE longitude. a) In which ocean is his ship? b) How might a global grid help ai ...
... world map. Suppose it is your job to send out rescue crews to save ships when they are in trouble. One day you receive a notice from a ship’s captain. He informs you that his location is approximately 20oS latitude and 80oE longitude. a) In which ocean is his ship? b) How might a global grid help ai ...
Journey Across Time
... • Next, read the labels at the top of each column and on the left side of the chart. ...
... • Next, read the labels at the top of each column and on the left side of the chart. ...
Lesson 4 Grid Reference Systems
... However, if you were to cut out 60 shapes identical to those in Figures 1.4.2 or 1.4.3, your globe would not be complete at either end. Each of these 60 grid zones lay between the 84 degrees north and the 80 degrees south lines of latitude. The polar regions would be missing. Therefore, to complete ...
... However, if you were to cut out 60 shapes identical to those in Figures 1.4.2 or 1.4.3, your globe would not be complete at either end. Each of these 60 grid zones lay between the 84 degrees north and the 80 degrees south lines of latitude. The polar regions would be missing. Therefore, to complete ...
Diagrams - Bardstown City Schools
... • Next, read the labels at the top of each column and on the left side of the chart. ...
... • Next, read the labels at the top of each column and on the left side of the chart. ...
Maps and Map Projections
... thousands of ways to transfer a spherical grid onto a flat surface to make a map projection, but no map projection can maintain all four of these properties at once. Because it is impossible to have all these properties on the same map, cartographers must decide which properties to preserve at the e ...
... thousands of ways to transfer a spherical grid onto a flat surface to make a map projection, but no map projection can maintain all four of these properties at once. Because it is impossible to have all these properties on the same map, cartographers must decide which properties to preserve at the e ...
Geodesic Discrete Global Grid Systems
... octants formed by the equator and prime meridian. Wickman et al. (1974) oriented the dodecahedron by placing the center of a face at the north pole and a vertex of that face on the prime meridian, thus aligning with the prime meridian an edge of one of the triangles created by stellating the dodecah ...
... octants formed by the equator and prime meridian. Wickman et al. (1974) oriented the dodecahedron by placing the center of a face at the north pole and a vertex of that face on the prime meridian, thus aligning with the prime meridian an edge of one of the triangles created by stellating the dodecah ...
Unit 3: Cities of the Eastern Hemisphere
... In this book, chapters devoted to developing the basic skills foundation are followed with a pretest activity and a final test. The pretests are designed in a completion format so students can be successful. The final tests are a multiple-choice format based on the pretest. Other chapters do not hav ...
... In this book, chapters devoted to developing the basic skills foundation are followed with a pretest activity and a final test. The pretests are designed in a completion format so students can be successful. The final tests are a multiple-choice format based on the pretest. Other chapters do not hav ...
GENERAL ARCHITECTURE DESIGN OF LUNAR PROJECTION SYSTEM
... The deformation of UTM projection is mainly determined by longitude difference. In order to ensure the map accuracy, UTM projection is suggested to adopt the method of zoning along the parallel 6°or 3°in the topographic map with basic scale, which is applied on earth in our country. UTM is better th ...
... The deformation of UTM projection is mainly determined by longitude difference. In order to ensure the map accuracy, UTM projection is suggested to adopt the method of zoning along the parallel 6°or 3°in the topographic map with basic scale, which is applied on earth in our country. UTM is better th ...
PowerPoint - Nutley Public School District
... • Location of a place when compared to other places. ...
... • Location of a place when compared to other places. ...
Longitude

Longitude (/ˈlɒndʒɨtjuːd/ or /ˈlɒndʒɨtuːd/, British also /ˈlɒŋɡɨtjuːd/), is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Points with the same longitude lie in lines running from the North Pole to the South Pole. By convention, one of these, the Prime Meridian, which passes through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, England, was intended to establish the position of zero degrees longitude. The longitude of other places was to be measured as the angle east or west from the Prime Meridian, ranging from 0° at the Prime Meridian to +180° eastward and −180° westward. Specifically, it is the angle between a plane containing the Prime Meridian and a plane containing the North Pole, South Pole and the location in question. (This forms a right-handed coordinate system with the z axis (right hand thumb) pointing from the Earth's center toward the North Pole and the x axis (right hand index finger) extending from Earth's center through the equator at the Prime Meridian.)A location's north–south position along a meridian is given by its latitude, which is (not quite exactly) the angle between the local vertical and the plane of the Equator.If the Earth were perfectly spherical and homogeneous, then longitude at a point would just be the angle between a vertical north–south plane through that point and the plane of the Greenwich meridian. Everywhere on Earth the vertical north–south plane would contain the Earth's axis. But the Earth is not homogeneous, and has mountains—which have gravity and so can shift the vertical plane away from the Earth's axis. The vertical north–south plane still intersects the plane of the Greenwich meridian at some angle; that angle is astronomical longitude, the longitude you calculate from star observations. The longitude shown on maps and GPS devices is the angle between the Greenwich plane and a not-quite-vertical plane through the point; the not-quite-vertical plane is perpendicular to the surface of the spheroid chosen to approximate the Earth's sea-level surface, rather than perpendicular to the sea-level surface itself.