* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth`s Oceans
El Niño–Southern Oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Atlantic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Challenger expedition wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
History of research ships wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean Research Group wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Marine habitats wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
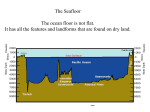
Oceans Cues World Oceans Seas Properties of Ocean Water Elements Salinity Sources Salinity Levels Gases Temperature Ocean Floor Edges of Continents Study the Ocean Floor Oceanographer The World’s Oceans 71% of the Earth’s surface is covered by ocean water. The oceans contain 97% of the earth’s water. All the oceans and seas are actually one continuous body of water. Oceans The oceans are the Atlantic, Pacific, Indian. Arctic and Southern. The Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean. The area and volume of the Pacific Ocean are greater than the Atlantic and Indian combined. Seas A sea is a part of an ocean that is nearly surrounded by water. The Mediterranean, Arctic and Black Sea are really part of the Atlantic Ocean. Properties of Ocean Water Ocean water is a mixture of gases and solids dissolved in pure water. Oceanographers believe oceans contain all the natural elements on Earth. 85 of 90 have been found in the ocean. Major Elements in the Ocean Ocean water is 96% pure water. Chlorine (1.9) and sodium (1.1) make up the next largest concentration of elements. Sodium chloride is table salt. Salinity Salinity describes the amount of dissolved water in the ocean. Salinity is expressed in parts per thousand. The salinity level of the ocean is expressed in parts per thousand. The average salinity of ocean is 35 parts per thousand. Sources of Salt in the Ocean When volcanoes erupt, rock materials and gases, such as chlorine, spew forth. As rivers, streams and glaciers move over rock and soil, they dissolve salts, such as magnesium, sodium and potassium, in them. As waves pound the shoreline, they dissolve salts from the rocks. Salinity Levels The salinity is lower in areas where freshwater rivers run into the ocean. Salinity levels are also affected by animals such as clams and oysters that use calcium salts to build their shells. They remove salt from the water. In warm ocean areas where there is little rainfall and much evaporation, the amount of dissolved salts is much greater. In polar regions, the salinity levels are high because temperatures are cold enough for ocean water to freeze. Pure water is removed and salts are left behind. Gases in Ocean Water The most abundant gases in ocean water are nitrogen, carbon dioxide and oxygen. The amounts of these elements vary with depth. They are more abundant at the ocean’s surface where sunlight causes more plant life. Temperature of Ocean Water Warm water holds less dissolved gas than cold water. When ocean water is cold, like in polar regions, it sinks and carries oxygen rich water to the ocean depths. As a result, fish and other animals can live in deep parts of the ocean. Temperature of Ocean Water Sun is the major source of heat for the ocean. Motions of the ocean, such as waves and currents, mix the surface water and transfer the heat downward. The Ocean Floor The topography of the ocean floor is different from the topography of the continents The Ocean Floor The ocean floor has higher mountains, deeper canyons, and larger flatter plains. Earthquakes occur more often. The rocks are very different. The crust is thinner. Edges of the Continents The shoreline is a boundary between where the land and the ocean meet. The area where the underwater edge meets of a continent meets the ocean floor is called a continental margin. Studying the Ocean Floor In 1872, the first expedition to explore the ocean began when the Challenger sailed from England. Scientists used wire to measure the ocean depth. Scientists aboard used nets to collect animals and plants from the ocean floor. Special thermometers measured the temperature. Samples of water were collected. Present Oceanographers Today oceanographers have modern instruments. Underwater cameras provide pictures of the ocean floor. Corers bring up samples of med and sand from the ocean bottom. Bathyspheres, bathscaphs and other submersibles are able to dive deep under the surface to explore Mapping the Ocean Floor One of the most important goals is to map the ocean floor. This is done by indirect methods such as echo sounding, radar, sonar and seismographic surveys. Echo Soundings All of these methods are based on the same principles. Energy waves are sent down to the floor are reflected and return to the surface, where they are recorded. Knowing the speed of sound, 1500 m per second, oceanographers can determine the depth. The most complete picture was gathered from information from a satellite, the Seasat, launched in 1978 Assignment Section 10.1 questions 1-6