* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 23 (Part 1)
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Bioinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Chemical biology wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
History of biotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene prediction wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
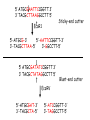
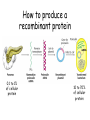
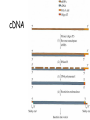
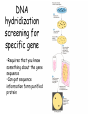
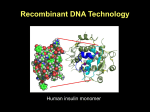
Chapter 23 (Part 1) Recombinant DNA Technology Cloning Vector Required features 1. Origin of replication 2. Selectable marker 3. Screenable marker for recombinant molecules 4. Cloning sites Restriction Modification System AAGATGCGAATTCGTACA DNA methylase AAGATGCGAATTCGTACA DNA methylase * * AAGATGCGAATTCGTACA AAGATGCGAATTCGTACA Restriction endonuclease Restriction endonuclease * * AAGATGCGAATTCGTACA AAGATGCG AATTCGTACA 5’ ATGCGAATTCCGGTT 3’ 3’ TACGCTTAAGGCCTT 5’ EcoR1 Sticky-end cutter 5’-ATGCG-3’ 5’-AATTCCGGTT-3’ 3’-TACGCTTAA-5’ 3’-GGCCTT-5’ 5’ ATGCGATATCCGGTT 3’ 3’ TACGCTATAGGCCTT 5’ Blunt-end cutter EcoRV 5’-ATGCGAT-3’ 3’-TACGCTA-5’ 5’-ATCCGGTT-3’ 3’-TAGGCCTT-5’ T4 DNA Ligase Transformation • All of the previous steps were performed in vitro. • We have generated a very small amount of a recombinant plasmid • Need to amplify in bacteria to get enough to work with. • Transformation – process to mobilize DNA into bacterial host • Select for transformed bacteria on specific antibiotic that corresponds to the antibiotic resistance gene present on the plasmid How to produce a recombinant protein 0.1 to 1% of cellular protein 10 to 70% of cellular protein cDNA cDNA Library cDNA DNA hydridization screening for specific gene •Requires that you know something about the gene sequence •Can get sequence information form purified protein Product name Protein type Application Company Adagen (Adenosine deaminase ) An enzyme Severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID) Enzon Genotropin (Recombinant growth hormone) A hormone Growth hormone deficiency (GHD) in children Pharmacia & Upjohn Humalog (Recombinant human insulin) A hormone Diabetes Eli Lilly Nabi-HB (AntiHepatitis B) An antibody Hepatitis-B Nabi Novo Seven (Recombinant coagulation factor VIIa) A modified factor Hemophillia patients with inhibitors Novo Nordisk Ontak (Diphtheria toxin-interleukin-2) A fusion protein Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) Ligand Pharmaceuticals Roferon-A (Recombinant interferon alfa-2a) A modifier Hairy cell leukemia or AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma Hoffmann-La Roche Genetic Modification of Higher Organisms • Can introduce gene into animals and plants • These modified organism are powerful research tools to study the effect of a specific gene product on metabolism, development etc…. • Has also been used to develop improved agricultural products Genetically Engineered Salmon Is Bigger Better? http://www.agwest.sk.ca/sabic_index_tp.shtml