* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells - VCE-Unit1and2Biology
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
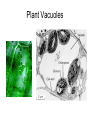
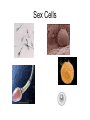
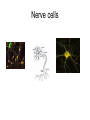
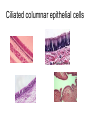
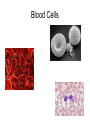
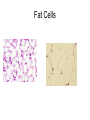
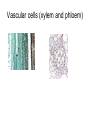
Cells Staining Cells • Staining is a technique used in microscopy to enhance contrast in the microscope image Mounting.. • refers to attaching the samples to a glass microscope slide for observation. • for samples of loose cells (e.g.blood or pap smear) the sample can be applied directly to a slide. • for larger tissues thinner sections are made Stains • Iodine – more contrast between cell structure. Also goes blue black when starch is present. • Methyl blue – stains nuclei blue Structure You were able to see the following in most cells under the light microscope • Cell wall • Cell Membrane • Cytoplasm • Nucleus • Vacuole • Plastids Structure • The following cell structures are only clearly visible through an electron microscope – Mitochondria – Golgi Apparatus – Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum – Rough Endoplasmic reticulum Cytoplasm • Cytosol –is the liquid part • Cytoplasm is the part that contains all the organelle structures Plant Vacuoles Plastids – organelles found in the cells of plants. • Chloroplasts – found in plants. Contain chlorophyll. Responsible for photosynthesis. • Leucoplasts – non-pigmented plastids found predominantly in the roots and non-photosynthetic parts of plants. They become specialised for bulk storage of starch (e.g.banana), protein and lipids. • Chromoplasts – for pigment synthesis and storage (e.g. red capsicum). Often found in fruits and flower part of plants. Cytoplasmic streaming • See wiki Protoctists or Protist • See wiki • P 83 of text • Be able to draw amoeba, euglena and paramecium. Book work • • • • • • Biological Drawings - 39-40 Kingdoms – 70; 79-83 Types of cells-71 Determining cell size - 72 Microscopes - 75-78 (overview) Cell structure 85-86 ( a lot of this is difficult but good exercise to attempt.) Prokaryotes • Bacteria produce enzymes that break down the organic matter into simpler substances that can then be absorbed by the bacteria. • Draw and label a generalised bacterial cell. Page 79 • How would you identify a bacterium? • Cell Size very tiny. See page 79 estimate size. Complete page 72 Cell Specialisation • Activity • Group the following into something that makes meaning to you? • Why did you group them this way? Cell Specialisation • Activity • Group the following into something that makes meaning to you? • Why did you group them this way? Cell Specialisation • Group them into animal and plant cells? • Can you identify any of these cells or what their function is ? What features did you use to categorise them. Cell Specialisation • Identify the following cells – The protista – – Identify the following specialised animal cells • Sex cells • Nerve cells • Muscle cells • Ciliated columnar epithelial cells • Red blood cells • White blood cells • Fat cells • Bone tissue Identify the following specialised plant cells • • • • • Cells from a leaf of a plant Stomata Cells that store starch e.g. banana cells Vascular cells (xylem and phloem) Cells with chromatoplasts Sex Cells Nerve cells Muscle cells Ciliated columnar epithelial cells Blood Cells Bone Tissue Fat Cells Plant Cells Leaf Cells Cells that store starch e.g. banana cells Vascular cells (xylem and phloem) Cells with chromoplasts