* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Viruses – Cellular Pirates
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
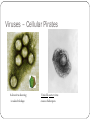
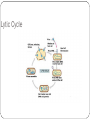
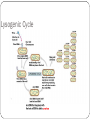
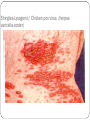
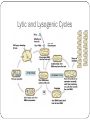
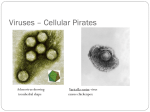
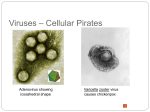
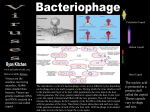
Viruses – Cellular Pirates Adenovirus showing icosahedral shape Varicella zoster virus causes chickenpox Characteristics of Viruses Obligate Intercellular Parasite - Must reproduce(replicate) inside a host Structure - Nucleic Acid – DNA or RNA - Protein coat – called a capsid - Envelope – some contain a layer of membrane taken from a host cell Mutate Rapidly Host Specific - can only infect one type of cell Small – from 20nm to 250nm - most are too small to be seen with a light microscope Virus Structure Bacteriophage Bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacteria - they are responsible for transduction in bacteria Viruses have two life cycles Lytic Cycle-Viruses-immediately infect the host cell Lysogenic Cycle - lay dormant in the cell Lytic Cycle Small Pox- Lytic Jenner developed first vaccine 1798 Lysogenic Cycle Herpes Simplex 1/Lysogenic Shingles-Lysogenic/ Chicken pox virus (herpes varicella-zoster) Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles Retroviruses Contain RNA and not DNA - to be able to take over a host cell, the retrovirus must be able to convert the RNA into DNA - to accomplish the conversion, retroviruses insert an enzyme called Reverse Transcriptase into the host cell Retroviruses Vocabulary Obligate intercellular parasite Capsid Envelope bacteriophage Lytic Cycle Lysogenic Cycle Phage prophage Retrovirus Reverse Transcriptase