* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
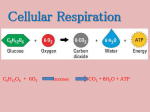
Biology I study guide for PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC Cellular Respiration 2015 Intended Learning Outcomes: Students should be able to… 1. For Escherichia coli do the following: a. describe 2-3 interesting facts (habitat, morphology, etc.). b. properly WRITE the scientific name. c. describe how to culture this bacterium. 2. Interpret a data table of biochemical tests and bacteria and determine the “unknown bacteria”. 3. Describe some of the “sterile techniques” used in this lab. 4. Know the location and function of each bacterial cell organelle. (7) a. Draw and/or interpret a diagram 5. Balance the overall equation of respiration (combustion) using any organic molecule (carbon source). Be sure to include the product of ATP and its reactants. 6. Be able to identify the 3 parts of ATP. a. identify where the ATP stores energy b. describe how ATP stores energy RESOURCES: Regular Biology: Quiz, Handouts, Practice Tests, Notes and Chapter 9 Honors Biology: Quiz, Handouts, Practice Tests, Notes and Chapter 7 Biology I study guide for PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC Cellular Respiration 2015 Intended Learning Outcomes: Students should be able to… 7. Explain and interpret diagrams of each of the following pathways: glycolysis, fermentation, Kreb’s cycle, and the electron transport chain by doing the following: a. start and end carbon sources (molecules) b. ATP used, produced, and net c. NADH (NADre) used, produced, and net d. FADH2 used, produced, and net e. reduction and oxidation of molecules. (Honors only) 8. Label a diagram of the electron transport chain 9. Be familiar with all key terms/terminology associated with this unit: ATP, prokaryotic, eukaryotic, aerobic, anaerobic, organelle and electron. 10. Short Answer: Choose one of the following ingredients found in many foods including energy drinks: Glucose, Riboflavin (vitamin B2), Niacin (vitamin B3), and Citric Acid. Explain how the one you chose helps to give us energy. 11. HONORS ONLY: For one of the biochemical tests, EXPLAIN how one of the enteric bacteria gave a positive result. RESOURCES: Regular Biology: Quiz, Handouts, Practice Tests, Notes and Chapter 9 Honors Biology: Quiz, Handouts, Practice Tests, Notes and Chapter 7 The product of glycolysis that diffuses into the mitochondrial matrix of eukaryotes for further breakdown is… a. acetyl CoA. b. pyruvic acid. c. oxaloacetic acid. d. citric acid. The starting substance of the Krebs cycle, which is regenerated at the end of the cycle, is a. b. c. d. acetyl CoA. pyruvic acid. oxaloacetic acid. citric acid. The Krebs cycle a. breaks down a two-carbon molecule into two molecules of CO2. b. produces a six-carbon molecule from six molecules of CO2. c. produces NADH from NAD+ and H+. d. generates most of the ATP produced in aerobic respiration. Glycolysis in prokaryotes takes place a. in the cytosol. b. in the mitochondria. c. only if oxygen is present. d. only if oxygen is absent. During glycolysis, glucose is… a. produced from two molecules of pyruvic acid. b. converted into two molecules of ATP. c. partially broken down and some of its stored energy is released. d. partially broken down and its stored energy is increased. Both lactic-acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation produce a. a two-carbon molecule from a six-carbon molecule. b. CO2 from a three-carbon molecule. c. ATP from ADP and phosphate. d. NAD+ and H+ from NADH. The electron transport chain is located predominantly in the: A. Outer membrane of the mitochondria B. Intermembrane space of the mitochondria C. Inner membrane of the mitochondria D. Matrix of the mitochondria E. Cytosol of the cell As an athlete's muscles are forced to work in the absence of enough oxygen, the muscle cells begin to produce… 1. 2. 3. 4. carbon dioxide ethyl alcohol lactic acid larger amounts of ATP GLUCOSE GLYCOLYSIS PYRUVATE LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION LACTIC ACID ALCOHOL FERMENTATION ETHANOL Hydrogen Ion Hydrogen Ion Hydrogen Ion FADH2 ADP + P NAD+ Electrons (Oxygen + Hydrogen => Water) Name ANSWER KEY Date____________Period____ C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 38ADP +38P 6CO2 + 6H2O + 38ATP Name of molecule in the can to the right that is used to start Cellular Respiration GLUCOSE Draw an arrow to the product above that’s produced during this part. Name of Part 1 GLYCOLYSIS Acetyl CoA Name of the molecules that make this process happen ENZYMES •Total Number of ATP produced? 4 •Any other energy products produced? NADH* Part 3 to be continued on the back. Name of Part 3:ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN Name of these 2 molecules which are the products of the first part of cellular respiration. PYRUVATE Name of the 4 carbon molecule OXALOACETATE Name of the energy molecules that will be used in part 3. NADH and FADH2 Name of Part 2 KREBS CYCLE # of ATP 2 Name of the 6 carbon molecule CITRATE What are the “waste products”? CO2 Name_______________________Date_________Period____ Name of this Process ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN Name of this? ENZYME, CHANNEL PROTEIN, PROTON PUMP, COMPLEX 1 NAD+ A: CELL MEMBRANE (PROK) INNER MEMBRANE OR CRISTAE (EUK) C: ATP SYNTHASE E: ATP G:CYTOSOL (PROK) MATRIX (EUK) Number of ATP produced 32-34 Number of ATP used 0 B:HYDROGEN OR PROTON(ion) D:ADP + P F WATER or ELECTRONS J:NADH Biology I study guide for PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC Cellular Respiration 2015 Intended Learning Outcomes: Students should be able to… 1. For Escherichia coli do the following: a. describe 2-3 interesting facts (habitat, morphology, etc.). b. properly WRITE the scientific name. c. describe how to culture this bacterium. 2. Interpret a data table of biochemical tests and bacteria and determine the “unknown bacteria”. 3. Describe some of the “sterile techniques” used in this lab. 4. Know the location and function of each bacterial cell organelle. (7) a. Draw and/or interpret a diagram 5. Balance the overall equation of respiration (combustion) using any organic molecule (carbon source). Be sure to include the product of ATP and its reactants. 6. Be able to identify the 3 parts of ATP. a. identify where the ATP stores energy b. describe how ATP stores energy 7. Explain and interpret diagrams of each of the following pathways: glycolysis, fermentation, Kreb’s cycle, and the electron transport chain by doing the following: a. start and end carbon sources (molecules) b. ATP used, produced, and net c. NADH (NADre) used, produced, and net d. FADH2 used, produced, and net e. reduction and oxidation of molecules. (Honors only) 8. Label a diagram of the electron transport chain 9. Be familiar with all key terms/terminology associated with this unit: ATP, prokaryotic, eukaryotic, aerobic, anaerobic, organelle and electron. 10. Short Answer: Choose one of the following ingredients found in many foods including energy drinks: Glucose, Riboflavin (vitamin B2), Niacin (vitamin B3), and Citric Acid. Explain how the one you chose helps to give us energy. 11. HONORS ONLY: For one of the biochemical tests, EXPLAIN how one of the enteric bacteria gave a positive result. RESOURCES: Regular Biology: Quiz, Handouts, Practice Tests, Notes and Chapter 9 Honors Biology: Quiz, Handouts, Practice Tests, Notes and Chapter 7