* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular respiration is the of food
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
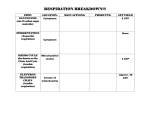
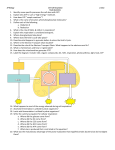
Biology Name ________________________ Date ________________ per _____ Aerobic Respiration Review Matrix Lactic Acid Charged Three ADP Cellular Respiration Two Oxygen Four Ethyl Alcohol ATP synthase Without oxygen Mitochondria CO2 Cytosol NAD+ Glucose Water Concentration Chemiosmosis PGAL Acetyl-CoA FADH Energy Uncharged Break down ATP Directions: Use the list of words above to fill in the blanks. Cellular respiration is the _________________ of food. This is how we release the ______________ from our food. The energy is stored in molecules called ______. Usually, the starting substance (food) for cellular respiration is ______________. This molecule is broken up into two molecules of ______________, each of which contains ______ carbon atoms. That first step of ________________ requires ___ATP. In the second step of glycolysis, 4 molecules of ______________ are produced. That step releases energy that is stored in the form of ____ATP. So, overall glycolysis has a net gain of ___ ATP. If no oxygen is available, the pyruvate is broken down into ______________ or ________________ and carbon dioxide. This is called anaerobic respiration or _________________. The entire process occurs in the ____________________ of the cell. If oxygen is available, the pyruvate enters a ________________________, where it loses a carbon atom as ___________ and becomes the two-carbon molecule ________________. The molecule enters the _________________. Electron shuttle molecules, _______________ and ______________ become _______________ as they accept electrons from the molecule going through the cycle. In addition, carbon dioxide is released and ____ ATP are produced during the Kreb's cycle. NADH and FADH are __________________ as they lose electrons to the electron transport chain. The electron transport chain generates a ________________ gradient of hydrogen ions. The electrons are accepted by, ___________________, the final electron acceptor, which then picks up hydrogens and becomes _____________. The hydrogen ions diffuse through the enzyme _______________ . That process is referred to as __________________. The ATP synthase uses the energy of the flowing hydrogen ions to phosphorylate __________, which becomes ___________. The ATP is then available to the cell to supply energy for activities. ATP becomes ________ as it supplies energy.