* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. The non-living synthesis of simple organic molecules. 2. The
Gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
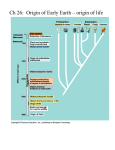
1. The non-living synthesis of simple organic molecules. Early Earth and oceans contained a mix of D1: Origin of Life on Earth inorganic molecules converted into simple organic molecules. These organic molecules may have been generated on the Earth or Space. 2. The assembly of these molecules into polymers Simple organic molecules polymerized into large complex organic chemicals 3. The origin of self-replicating molecules made inheritance possible. Karl Popper argues that an hypothesis is not scientific if it cannot be shown to be false. So is the Origin of Life on Earth of “Scientific value”? Gases from the interior escaped by volcanoes, forming an atmosphere of Hydrogen (H), Water vapour (H2O), Methane (CH4), Ammonium (NH4), Nitrogen (N2), Sulfuric Acid (H2S) – there was no oxygen (O2). The mix of chemicals present in the oceans is called primeval/primeordial soup or sea. DNA and RNA can act as templates for copying RNA self-replication does not require proteins/enzymes Self-replicating molecules are subject to evolution by natural selection 4. The packaging of these molecules into membranes with an internal chemistry different from their surroundings Formation of closed membranes is believed to be an early and important event in the origin of cellular life Closed membrane vesicles form spontaneously from lipids separating inside from outside Internal cellular metabolism then developed The Earth was formed about 4.5 billion years ago from dust around the Sun. As the dust gathered size, gravity and radioactive decay generated heat which melted the center producing a core or molten Iron and nickel surrounded by a cooler liquid mantle. On top of the mantle is a crust which formed the continents and sea floor. This is called a Reducing Atmosphere Miller and Urey conducted experiments in 1953 to see whether Chemical Evolution could occur in primeval soup. Chemical evolution is the sum of the pre- biological changes that transformed simple atoms and molecules into the more complex chemicals needed for life. Miller and Urey were able to form organic compounds and amino acids and the nucleotide base adenine! Panspermia – hypothesis that life on Earth may have originated by the introduction of complex organic chemicals or even bacteria via comets. Cosmic radiation in deep space may provide the energy to form complex organic molecules. How did Amino Acids and nucleotides polymerize to form proteins and nucleic acids Water favours polymer hydrolysis Hydrothermal vents on seafloors called black smokers allow superheated water from the earth`s crust to enter the ocean. Black smokers are rich in dissolved sulfides Volcanoes help by fixing nitrogen for use by early bacteria Mars – because mars is small, it cooled quickly which may have permitted prebiotic evolution. Martian meteorites may have brought these compounds to Earth. RNA World Hypothesis – RNA played an important role in the origin of life because it is capable of storing information and of replicating it 2. When RNA is replicated, mutations occur which leads to variation, natural selection and this evolution. 1. Ribozymes are small sequences of RNA that act as enzymes to catalyse reactions of RNA replication RNA may have generated the first proteins Eventually, RNA was replaced by DNA and enzymes Overtime, the complexity of organic compounds in the primeval soup increased. Coacervate – aggregations of polymers Protobionts – the first precursors to cells Protobionts may have evolved from coacervates containing RNA An internal environment can be maintained separate from the external environment A major transition in evolution occurred when bacteria evolved to contain chlorophyll which allowed photosynthesis to occur and high levels of oxygen were produced. This is the Oxygen Catastrophe (2 billion years ago) This lead to a layer of ozone (O3) forming in the upper atmosphere – this was a protective layer from UV rays from the sun but it also stopped the production of new organic chemicals in the primeval sea Endosymbiotic Theory – Chloroplasts and mitochondria are derived from free-living prokaryotic ancestors then they were engulfed by larger prokaryotes Evidence for the Endosymbiotic Theory: M and C contain DNA M and C are surrounded by double membranes New M and C are formed by a process that resembles binary fission Internal structure and biochemistry of chloroplasts are very similar to cyanobacteria M and C contain ribosomes like bacterial ones (70s) Mitochondria evolved from Proteobacteria Chloroplasts evolved from cyanobacteria http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Vgh2Eb8E2g http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3H0RXDrf yZc http://www.allthingsscience.com/video/677/O rigin-of-Life--Panspermia-1-of-3