* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution of cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
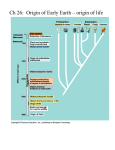
Evolution of cells Prof. Dr. Müjgan Cengiz Evolution of cells Cells divided to two main class Procaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Some basic molecular mechanisms takes place in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes 1-Formation of substance 2-Atomic Evolution 3-Molecular Evolution 4-Cellular Evolution Life originated . 3.5-3.8 bilion years Ago. 1 bilion years After earth was Formed. İn 1920 it was tought simple organic molecules could form Spontaneously polymerized into macromolecules like pirimitive earth atmosphere. At that time there are O2 H2, , H2S ,CO at the atmosphere In this condition by the aid of energy of sunligt or electricel discharge organic molecules can form spontaneously. In 1950 first demonstration by Stanley Miller Discharge of electrical sparks to the mixture of Hydrogen, methane, amonia And water cause synthesis of organic molecules. The reaction products are amino acids alanine,aspartic acid,glutamic acid,glycine, Some other organic molecules such as urea,lactic acid,acetic acid,formic acid. The other step in evolution was the formation of macromolecules. In the cells there are two informational maromolecules present(nucleic acids and proteins) The nucleic acids can make their own self replication. They can serve as templates of own sythesis. In 1980s Altman found RNA capable of some chemical reactions(polymerization of nucleotides) RNA is uniquely able to serve a template and catalyzes its own replication. The interaction between the RNA and proteins evolved present day genetic code. The first genetic material was RNA. Today after investigaton of reverse transkriptase enzyme it can be explained how DNA replaced RNA as the genetic material. Phospholipids Main component of membranes Phosphate at outside and reacted with water Hydrocarbon tails are inside Bilayer stabilized barier The first cell formed by enclosing self replicating RNA by a membrane EVOLUTİON OF THE METABOLİSM The cells originated from the sea organic molecules, they were able to obtain the organic molecules, food from the sea and environment. They need to generate the energy from environmet and synthetize molecule for their replication. The cells use ATP for their source of energy.The mechanism for generation of energy have evolved in 3 stages. Glycolysis, photosynthesis and oxidative metabolism. In anaerobic conditions it is assumed that the first energy generating reactions were like anaerobic glycolysis, the breakdown of organic molecules at anaerobic conditions. Breakdown of glucose to lactic acid generates 2 ATP. The development of photosynthesis is the second evolutionary step. This allows taking energy from sunligt and making the energy independently from organic substances. The release of O2 as a result of photosynthesis, changed the environment and led to development of oxidative metabolism. Complete breakdown of glucose to CO2 and H2O yields energy 36 to 38 ATP. Procaryotes are the most different organisms and they obtain their energy from inorganic chemicals (for example from hydrothermal events deep ocean floor,soil). DNA sequence comparison showed three were distinct branch of tree of life. Archabacteria and bacteria are small unicelular organisms and have 1000-4000 genes. Many of the genes from within a single organisms show family resemblence. Family resemblence are seen in 200 gene of three main acester family of the living world. There are three lines of cells(archabacteria,eubacteria and eukaryotes) Mitochondria and chloroplasts are originated from endosymbiotic association of aerobic bacteria and cyanobacteria with the ancestor of eukaryotes. Why earth? Life exists only at earth Chemical reactions occurs only at liquid medium o Jüpiter -15 C o Satürn -180 C o Merkür 430 C o Venüs 480 C The size and mass of earth Small planets can not take the atmosphere Big planets have dense atmosphere Atmosphere is important for radiation Photosynthesis needs visible light Evolution and survive of primitive cell needs energy Heterotroph Takes the energy and building structure from environment All animals prokaryotes Fungies Autotroph They can feed themselves They synthetize the organic compounds from simple inorganic substances and sunlight for the energy need All plants Some prokaryotes Chemosynthetic They supply the energy for synthetize the organic compounds from simple inorganic reactions First animals, fungies and single cell organisms are heterotroph. When the number of cells increased, amount of molecules that need decreased. A competition begin between cells Some cells begin to synthetize organic substances from inorganic substances First living primitive cell is chemosynthetic or photosynthetic autotroph. In marshy place and oceans pirimitive chemosynthetic bacteria. The main topic in evolution is mutation (mutation is a obligation in breeding) Natural selection Viruses Genetic recombination Transpozons Gene duplication