* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Thomas Tallis Science
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
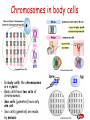
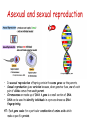
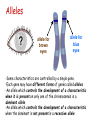
Inheritance • • • • • Make sure you revise: Mitosis - cell division Meiosis – produces sex cells Genes and chromosomes Inherited disorders Embryo screening • HT: stages of meiosis Mitosis parent cell mitosis daughter cells Body cells divide by mitosis. When a body cell divides by mitosis: • Copies of the genetic material are made first • Then two genetically identical body cells are produced Higher Tier – Meiosis and key terms Chromosomes in body cells • In body cells the chromosomes are in pairs • Body cells have two sets of chromosomes; • Sex cells (gametes) have only one set. • Sex cells (gametes) are made by meiosis Asexual and sexual reproduction • • • • In asexual reproduction offspring contain the same genes as the parents. Sexual reproduction gives variation because, when gametes fuse, one of each pair of alleles comes from each parent. Chromosomes are made up of DNA. A gene is a small section of DNA. DNA can be used to identify individuals in a process known as DNA fingerprinting. HT: Each gene codes for a particular combination of amino acids which make a specific protein. Alleles ? allele for brown eyes allele for blue eyes •Some characteristics are controlled by a single gene. •Each gene may have different forms of genes called alleles •An allele which controls the development of a characteristic when it is present on only one of the chromosomes is a dominant allele. •An allele which controls the development of a characteristic when the dominant is not present is a recessive allele Determining the sex of a child • In females the sex chromosomes are the same (XX) • In males the sex chromosomes are different (XY). Genetic diagrams/Punnet squares Eg, the allele for brown eyes (B) is dominant to the allele for blue eyes (b) If 2 parents have brown eyes and have the genetic make up Bb, what would be the chance of them having a blue-eyed child? B b 75% chance brown eyed child B 25% blue eyed child BB Bb (brown eyes = (brown eyes = 25%) 25%)) b Bb (brown eyes = 25%) bb (blue eyes = 25%) Gregor Johann Mendel Question Answer Who was Gregor Mendel? An Austrian monk who discovered how characteristics were inherited. What experiments did he do? Cross-bred pea plants and counted the different types of offspring. What did he discover from his findings? That characteristics were inherited in clear and predictable patterns (idea of inherited ‘factors’). That some characteristics were dominant over others and that they did not ‘mix’ together. Why did people not accept his ideas at the time? Genes and chromosomes had not yet been discovered so people didn’t understand his theories. When and why were Mendel's ideas finally accepted? By 1900 people had seen chromosomes through a microscope. Three scientists found Mendel’s papers and repeated his experiments leading to further developments into genetics and Mendel's work. Punnet squares What are inherited diseases? Inherited diseases are diseases caused by faulty genetic material that is passed on to future generations. They are sometimes called genetic disorders. Many inherited diseases are caused by mutations in DNA, resulting in faulty alleles that are not properly expressed. Mutations can be spontaneous or caused by exposure to mutagens such as radiation and certain chemicals. There are over 4,000 known inherited diseases, although the specific alleles involved are only known for 25% of them. Polydactyly Polydactyly – having extra fingers or toes – is caused by a dominant allele of a gene and can therefore be passed on by only one parent who has the disorder Cystic fibrosis summary • A disorder which affects cell membranes in many organs of the body particularly the lungs and the pancreas • Caused by a recessive allele so must be inherited by both parents Cystic fibrosis Embryo screening • Embryos can be screened for the alleles that cause these and other genetic disorders.