* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hemophilia
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
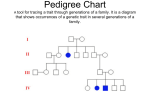
Hemophilia By: Abijah Minton Alfredo Sugawara Brandon Abad Summary of Hemophilia Hemophilia is a disorder where your blood doesn’t clot. It is a recessive trait. If a mom doesn’t have the gene for hemophilia and the father does, their son will not carry the trait for hemophilia but their daughter will. Symptoms of hemophilia are excessive bleeding. Other people may experience life threatening hemorrhages with common What Chromosome is your disorder located on? This disorder is located on the x chromosome. Mode of Inheritance Someone would acquire hemophilia from sex linked traits. If a trait is sex linked, then a gene is only carried by the male or female parent. Not by both. Explaining Alleles An allele is any of several forms of a gene, usually arising through mutation, that are responsible for hereditary variation. Alleles come from a female and male parent. RR stands for dominant alleles. rr is a recessive allele. Rr is the dominant gene over the recessive gene. The dominant gene produces the same phenotype in the organism whether or not its allele identical. The recessive gene produces its characteristic phenotype only when its allele is identical. Probability of Passing Down Hemophilia H h h h Hh Hh hh hh H H h h HH Hh Hh hh Probability Using Ratios And Percentages Ratios 2 :2 Hh : hh Percentage 50% : 50% 50% Hh : 50% hh Hh Hh hh hh Explanations A capital H means that the allele for Hemophilia is dominant, where as a lowercase h means recessive. HH: Not Hemophilia, Hh: Not Hemophilia, hh: Hemophilia HH: Homozygous Dominant, Hh: Heterozygous Recessive, hh: Homozygous Recessive Genotype And Phenotype Probability Phenotype – Ratio: 2 Hemophiliacs to 2 Non- Hemophiliacs – Percentage: 50% to 50% Genotype – Ratio: 2 Hh to 2 hh - Percentage: 50% Hh to 50% hh Student Practice Genotype: H h H HH Hh h Hh hh Ratio: 1 : 2 : 1 Percentage: 25% : 50% : 25% Phenotype: Ratio: 3 : 1 Percentage: 75% : 25% Hypothetical Pedigree Key Female Hemophiliac Female Male Hemophiliac Male Key Male Hemophiliac Male Female Hemophiliac Student Practice Female 2. How many females in this pedigree have hemophilia? 3 1. Out of the second generation siblings, what is the ratio of hemophiliacs to non-hemophiliacs? 3. How many males in this pedigree have hemophilia? 2 2:1