* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6: Genetic diseases
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
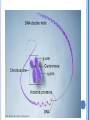
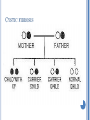
CHAPTER 6: GENETIC DISEASES INTRODUCTION Cystic fibrosis: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Twjg7v-pTO4 WHAT ARE GENETIC DISEASES/DISORDERS? A genetic disorder is an illness caused by abnormalities in genes or chromosomes What are chromosomes? CHROMOSOMES A normal human being has 46 of these chromosomes in each cell (excepting reproductive cells) Of these 46 chromosomes, 44 are ‘autosomal’ 2 chromosomes are ‘sex chromosomes’ X and Y GENETIC DISORDERS Sometimes genetic disorders are caused by a whole chromosome:: Down syndrome Klinefelter syndrome Down syndrome is caused by a trisomy: Instead of a pair of chromosomes, you have 3 In this case 21 Down syndrome is also called ‘trisomy 23’. Other trisomies can occur, but often result in a miscarriage For example: trisomy 16 TRISOMIES The most common types of autosomal trisomy that survive to birth in humans are: Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome) Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome) Trisomy 9 Trisomy 8 (Warkany syndrome 2) Trisomy 22 Sometimes, there is an extra copy of a sex chromosome present: XXX, XXY or XYY (XYY is not really a disorder) Klinefelter syndrome is an example: XXY GENETIC DISORDERS Other genetic disorders are not caused by a whole chromosome, but by a fault in one or more genes A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a polypeptide or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. GENES http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8s4he3wLgkM Cystic fibrosis is an example of a disorder caused by only 1 faulty gene You can only get it when this faulty gene is present on both chromosomes of chromosome 7 If only one chromosome 7 has the faulty gene you are a carrier You don’t get ill because the normal gene is dominant over the faulty gene CYSTIC FIBROSIS HUNTINGTON’S DISEASE Cystic fibrosis is caused by a recessive (nondominant) gene Some genetic disorders are caused by faulty genes that are dominant Huntington’s disease In this case you will get the disease, even if only one copy of your chromosome 4 has the gene http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4HgFUvVyHY Q WORK Read pages 76 – 78 Answer questions 1 - 6