* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Iron-sulfur proteins
Chloroplast DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Flavin adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
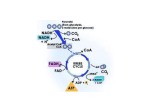
p691 Only those with specific transporters can pass N side All pathways related to fuel oxidation except glycolysis Oxidative phosphorylation • Converting the energy from electrons (from NADH and FADH2) to ATP • Electron transfer occurs in oxidative phosphorylation: 1. Direct transfer to reduce cation, Fe3+ Fe2+ 2. Transfer as hydrogen atom 3. Transfer as hydride ion (:H-) Five electron carrying molecules 1. NAD+ 2. FAD 3. Ubiquinone 4. Cytochromes 5. Iron-sulfur proteins Ubiquinone (coenzyme Q; Q) Ubiquinone Plastoquinone (plant chloroplast) Menaquinone (bacteria) p693 cytochromes p694 Iron-sulfur proteins Iron-sulfur proteins p695 Method for determining the sequence of electron carriers p696 p696 p705 Oxidative phosphorylation Complex I NADH +H+ NAD+ FMN Fe2+S CoQ FMNH2 Fe3+S CoQH2 p698 NADH +H++Q --> NAD++QH2 4 protons pump out Complex I & II Succinate FAD Fe2+S CoQ Fumarate FADH2 Fe3+S CoQH p697 Complex III p700 CoQH2 cyt b ox Fe2+S cyt c1 ox cytcred CoQ cytbred Fe3+S cytc1red cytcox QH2+2Cytc1oxidized+2HN+ --> Q+2Cytc1reduced+4Hp+ Complex IV cyt c red cyt a ox cyt a3 red O2 cyt c ox cyt a red cyt a3 ox 2 H2O p702 4Cytcreduced+8HN++O2 --> 4Cytcoxidized+ 4Hp++2H2O p703 p703 p706 QH2 oxidase (resistant to cyanide) p675 p698 Chemical uncouplers p707 • Chemicals like DNP and FCCP are weak acid with hydrophobic properties that permit them to diffuse readily across mitochondrial membranes. After entering the matrix in the protonated form, they can release a proton, thus disspating the proton gradient. p406 Ionophores • Valinomycin (an ionophore) allows inorganic ions to pass easily through membranes. This will uncouple electron transfer from oxidative phosphorylation. Mitochondrial ATP synthase complex p711 NADH transport • NADH produced by glycolysis must be transported into mitochondria to produce ATP. • However, NADH cannot enter mitochondria directly. Instead it is transported by the form of malate or glycerol 3-phosphate. Malate-aspartate shuttle p715 Glycerol 3-phosphate shuttle p715 Oxidative phosphorylation in brown fat tissue is uncoupled with ATP synthesis p687 Regulation p718 Mitochondrial genome p720 Mitochondrial encephalomyopathies • Mutations in mitochondrial genes cause mitochondrial encephalomyopathies that affecting primarily the brain and skeletal muscle. Because infants inherit their mitochondria from their mothers, so mitochondrial encephalomyopathies are maternal-linked. Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) • LHON is the result of defective mitochondrial genes that are involved in electron transfer. • Vision loss usually occurs between the ages of 15 and 35. Myoclonic epilepsy and raggedred fiber disease (MERRF) • Mutation in the mitochondrial gene that encodes a tRNA specific for lysine (lysyl-tRNA) results in MERRF. • Synthesis of several proteins require this tRNA is interrupted. p720 MERRF • MERRF patients often have abnormally shaped mitochondria containing paracrystalline structures. • This lysyl-tRNA mutation is also one of the causes of adultonset (type II) diabetes. Many respriatory proteins are encoded by mitochondria Mitochondrion is probably evolved from endosymbiotic bacteria p35 Bacteria do have respiratory chain enzymes • For example, E. coli has NAD-linked electron transfer from substrate to O2, coupled to the phosphorylation of cytosolic ADP. Mitochondria, apoptosis, and oxidative stress Mitochondria is not only involved in ATP synthesis. It is also involved in cellular damage and death. The role of mitochondria in apoptosis • When cell receives a signal for apoptosis, one consequence is the permeability of the outer mitochondrial membrane will increase, allowing cytochrome c release. • The release of cytochrome c will activate caspase 9, which will initiate the protein degradation process. Mitochondria can produce superoxide free radical Mitochondria and oxidative stress • Antimycin A inhibits complex III by occupying the QN site, which may increase the likelihood of superoxide radical formation and cellular damage. The role of mitochondria in oxidative stress PPP