* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 18.4
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
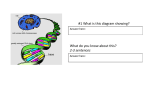
Section 18.4 Heredity Heredity Objectives Explain how genetic information passes from one generation to the next. Identify the causes of genetic disorders. Compare the role of genes, environment, and behavior in affecting a person’s risk for disease. Slide 1 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity Quick Quiz Take a brief self-inventory of some of your physical traits, or characteristics. Do you have a widow’s peak or a smooth hairline? Widow’s Peak Smooth Do you have free or attached earlobes? Free Attached A widow’s peak and free earlobes are examples of dominant traits. What do you think a “dominant trait” is? Switch to QuickTake version of the quiz. Slide 2 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity The Basic Rules of Heredity • Children's eye color, the shape of their ears, and their height are all determined in part from the genetic information they inherit from their parents. • Heredity is the passing on, or transmission, of biological traits from parent to child. Slide 3 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity Chromosomes • Chromosomes (KROH muh sohmz) are tiny structures found within cells that carry information about the characteristics you will inherit. • Most of the cells in your body contain 23 pairs of chromosomes. • When a sperm and egg unite, the fertilized egg ends up with 46 chromosomes—23 from each parent. Slide 4 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity Genes • A gene is a section of a chromosome that determines or affects a characteristic, or trait. • Genes come in pairs. • Hereditary information passes from one generation to the next through genes contained on the two sets of chromosomes that a person receives from their parents. Slide 5 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity Dominant and Recessive Traits • A dominant trait is one that appears in an offspring whenever its gene is present. • A recessive trait appears in an offspring only when the dominant form of the gene is not present. • The rules of heredity for most traits are complex. Slide 6 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity Heredity and Disease • Just like earlobe shape, eye color, and other inherited traits, an abnormal condition known as a genetic disorder can be passed from parent to child. • Genetic disorders are caused by the inheritance of an abnormal gene or chromosome. Slide 7 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity Genetic Disorders • Many genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis and hemophilia, are recessive traits. • A few disorders, such as Huntington’s disease, are dominant traits. • Other genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome, are the result of too few or too many chromosomes. Slide 8 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity Slide 9 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity For: Updates on genetic disorders Click above to go online. Slide 10 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity Diseases With a Genetic Link • Scientists know that a person’s risk for many diseases increases when close relatives have the disease. • Some diseases for which a genetic link is suspected or has been identified are • breast cancer • colon cancer • high blood pressure • diabetes • some forms of Alzheimer’s disease • Many different genes affect the development of disease. Slide 11 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity The Effect of Environment and Behavior • For most diseases, your environment and your behavior affect your risk as much as or even more than your genes. • Exposure to environmental risk factors is sometimes not in your control. • Among the factors you can control are your habits or behaviors. • Making wise choices now will greatly decrease your risk for disease later on in life. Slide 12 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity Slide 13 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity Medical Advances • Genetic Testing Genetic testing involves the analysis of a blood sample for the presence of abnormalities in specific genes. • Gene Therapy Scientists are currently researching a technique in which healthy copies of a gene are delivered to the cells of a person who has a defective copy of the gene. Slide 14 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity Vocabulary heredity All the traits that are passed from parent to child; the biological process of passing on, or transmitting, those traits. chromosome The tiny structures found within cells that carry information about inherited characteristics. gene A section of a chromosome that determines or affects a characteristic, or trait. genetic disorder A disorder caused by the inheritance of an abnormal gene or chromosome. Slide 15 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity QuickTake Quiz Click to start quiz. Slide 16 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity For: Chapter 18 self test Click above to go online. Slide 17 of 17 Section 18.4 Heredity End of Section 18.4 Click on this slide to end this presentation. Slide 18 of 17