* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chromosomes & Inheritance
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
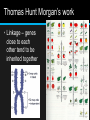
Chromosomes & Inheritance Chapter 13 Raven & Johnson Chapter 15 Campbell Mendel & Genes • 1902 – Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance • Genes have specific loci on chromosomes – chromosomes divide and move Thomas Hunt Morgan’s work • Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly) • Normal phenotype – wild type – red eyes • Mutant phenotype – white eyes • Discovered through mating that white eyes was sex linked • Gene located on sex chromosome Thomas Hunt Morgan’s Work Thomas Hunt Morgan’s work • If on X chromosome, females need two copies to express recessive gene • Males need only one (they are XY) • Females with one – carrier (can pass on) Thomas Hunt Morgan’s work • Linkage – genes close to each other tend to be inherited together Genetic Recombination • Production of offspring with new combinations of traits inherited from two parents • If unlinked, there is a 50% frequency of recombination Completely linked have no recombinants – 0% frequency If normally linked, then crossing over could break the linkage and raise the frequency Genetic Mapping • Alfred Sturtevant • The farther apart two genes are on a chromosome, the more chances that crossing over can occur and the higher the recombinant frequency will be • Can use frequency numbers to map the distance and order of genes – linkage map Genetic Mapping • Testcross design to map the relative position of three fruit fly genes, body color (b), wing size (vg), and eye color (cn). • The recombination frequency between cn and b is 9%. • The r.f. between cn and vg is 9.5%. • The r.f. between b and vg is 17%. Genetic Mapping • The only possible arrangement eye color gene between the other two • Map unit – distance between genes (1 m.u. = 1% recombination frequency) • Distances are added Sex Chromosomes • XX – female • XY – male • Determined by sperm (X or Y) • Sex linked – usually on X & recessive • Fathers pass to all daughters but no sons • Mothers can pass to either Sex Chromosomes • Ex - colorblindness Sex-linked Disorders • Dechenne muscular dystrophy • Progressive muscle weakness • Missing protein (dystrophin) • Hemophilia • Absence of protein for blood clotting X-Inactivation • Females have two X chromosomes, but one inactivates during embryo development • Condenses into Barr body • So only one X functions in males AND females • Occurs when –CH3 groups are added to cytosine • Gene on inactive X makes this happen • A lot more to figure out Chromosome Errors • Nondisjunction – homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids do not split evenly into gametes • Result – some have more, some have less • Abnormal chromosome # - aneuploidy • Extra copy – trisomic • 1 copy missing – monosomic • Extra full sets – polyploidy (occurs in plants) Chromosome Errors • Deletion – missing part • Duplication – extra piece Chromosome Errors • Inversion – reversal • Translocation – out of order Resulting Problems • Many result in spontaneous abortion • Down syndrome • Trisomy 21 • Specific symptoms • Correlation with maternal age • Result of nondisjunction during meiosis I Resulting Problems • XXY – Kleinfelter’s syndrome • XO – Turner syndrome • Deletion at #5 – cri du chat • Translocations – some cancers • Fragile X – abnormally thin section of DNA on X chromosome • Symptoms are different if from sperm or egg (worse if from egg) FYI…Cytoplasmic genes • Genes found on DNA of mitochondria and chloroplasts (not nucleus) do not follow all the rules