* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TOPIC: Applied Genetics AIM: What methods can be used to
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
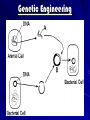
TOPIC: Applied Genetics AIM: What methods can be used to develop organisms with desirable traits? Do Now: List and explain two ways genetic disorders can be detected. What are 3 methods used to develop organisms with desirable traits? SELECTIVE BREEDING CLONING GENETIC ENGINEERING What is selective breeding? The crossing of plants or animals that have desirable traits to make offspring with those same traits 2 types: – hybridization – inbreeding Selective Breeding: A case study Selective Breeding: A case study Hybridization Crossing 2 genetically different but related species HYBRID = new offspring Best of both parents Example: horse + donkey mule (hybrid) Hybridization Braham cattle: good resistance to heat but poor beef Shorthorn cattle: good beef but poor heat resistance Santa Gertrudis cattle: formed by crossing Braham and shorthorn good heat resistance and beef Hybridization Jaglion = jaguar + lion Hybridization Tigon = male tiger + female lion Hybridization Liger = male lion + female tiger Hybridization TOPIC: Applied Genetics AIM: What is cloning? Do Now: Why is hybridization a form of selective breeding? Advantages Crossing plants or animals that have the same or very similar characteristics Pass on/preserve good traits Disadvantages Offspring are: Inbreeding – Smaller and weaker – More susceptible to diseases – More prone to genetic disorders Cloning Technique used to produce offspring with desired traits Clone Organism that is genetically identical to the organism from which it is produced (same genes) Cloning Dolly = 1st cloning of an adult mammal (sheep) 1997 Idaho Gem = 1st cloned mule (MAY 2003) Cloned from a champion racing mule CopyCat (Cc) = 1st cloned cat (2002) What is genetic engineering? Process in which genes (pieces of DNA) from one organism are transferred into another organism Making changes in the DNA of an organism “ gene splicing” What is recombinant DNA? Combined DNA (from 2 organisms) DNA from complex organism is cut and placed into the DNA of a simple organism Simple cells with recombinant DNA can produce proteins made in the complex organism Example: Inserting human DNA into bacterial cell DNA bacteria cell can produce insulin What is a plasmid? Ring of DNA in bacteria Genetic Engineering (plasmid) (Recombinant DNA) What can genetic engineering be used to produce? Insulin Human growth hormone Hepatitis B vaccine Interferons To improve food crops Proteins for blood clotting