* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WELCOME BACK! Time to jump start your brain!
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
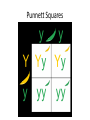
WELCOME BACK! Time to jump start your brain! • What’s the purpose of mitosis? • What’s the purpose of meiosis? • How many chromosomes do somatic cells have? • How many chromosomes do gametes have? Heredity and Genetics Mendel and Our Understanding of the Gene Pool Gregor Mendel • Gregor Mendel was an Augustinian friar who enjoyed gardening and science • Though people had an idea about how traits were passed from parent offspring, it was Gregor Mendel who proved it using science • Between 1856 and 1863, he raised pea plants, which he used to study genetic inheritance • He is now known as the “Father of Genetics” What did Mendel prove? • The Law of Segregation - The two members of a gene pair (alleles) segregate (separate) from each other in the formation of gametes. Half the gametes carry one allele, and the other half carry the other allele. • The Law of Independent Assortment - Genes for different traits assort independently of one another in the formation of gametes. The Experiment • There are three things that Mendel paid attention to in his experimental design: – He controlled over breeding – He used purebred plants – He observed only either/or traits, or traits that manifest in only two forms • He followed 7 traits: pea shape, pea color, flower color, flower position, pod shape, pod color, plant height Vocab Check • A gene is a piece of DNA that provides a set of instructions to a cell to make a certain protein. • An allele is any of the alternative forms of the gene that may occur. • A genome is all of an organism’s genetic information. Punnett Squares Types of Crosses • Monohybrid Cross – involves the crossing of only one trait – Test Cross – A cross between an unknown genotype and a recessive phenotype Types of Crosses • Dihybrid Cross – involves the crossing of two different traits Mendel’s Second Law • The Law of Independent Assortment – states that allele pairs separate independently of each other during gamete formation (meiosis) Heredity Probabilities • Probability is the likelihood that an event will occur Genetic Variation • One of the benefits of sexual reproduction (over asexual reproduction) is that it provides for abundant variation. • There can be 8 million different combinations of chromosomes produced through meiosis. • Crossing over occurs when homologous chromosomes exchange segments during meiosis. Genetic Variation • Each chromosomes contains hundreds of genes • How do genes show independent assortment if they are on the same chromosome? • Genes located close together on the same chromosome are said to display genetic linkage.