* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WELCOME BACK! Time to jump start your brain!
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
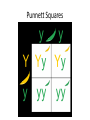
WELCOME BACK! Time to jump start your brain! • What’s the purpose of mitosis? • What’s the purpose of meiosis? • How many chromosomes do somatic cells have? • How many chromosomes do gametes have? Heredity and Genetics Mendel and Our Understanding of the Gene Pool Gregor Mendel • Gregor Mendel was an Augustinian friar who enjoyed gardening and science • Though people had an idea about how traits were passed from parent offspring, it was Gregor Mendel who proved it using science • Between 1856 and 1863, he raised pea plants, which he used to study genetic inheritance • He is now known as the “Father of Genetics” What did Mendel prove? • The Law of Segregation - The two members of a gene pair (alleles) segregate (separate) from each other in the formation of gametes. Half the gametes carry one allele, and the other half carry the other allele. • The Law of Independent Assortment - Genes for different traits assort independently of one another in the formation of gametes. The Experiment • There are three things that Mendel paid attention to in his experimental design: – He controlled over breeding – He used purebred plants – He observed only either/or traits, or traits that manifest in only two forms • He followed 7 traits: pea shape, pea color, flower color, flower position, pod shape, pod color, plant height Vocab Check • A gene is a piece of DNA that provides a set of instructions to a cell to make a certain protein. • An allele is any of the alternative forms of the gene that may occur. • A genome is all of an organism’s genetic information. Punnett Squares Types of Crosses • Monohybrid Cross – involves the crossing of only one trait – Test Cross – A cross between an unknown genotype and a recessive phenotype Types of Crosses • Dihybrid Cross – involves the crossing of two different traits Mendel’s Second Law • The Law of Independent Assortment – states that allele pairs separate independently of each other during gamete formation (meiosis) Heredity Probabilities • Probability is the likelihood that an event will occur Genetic Variation • One of the benefits of sexual reproduction (over asexual reproduction) is that it provides for abundant variation. • There can be 8 million different combinations of chromosomes produced through meiosis. • Crossing over occurs when homologous chromosomes exchange segments during meiosis. Genetic Variation • Each chromosomes contains hundreds of genes • How do genes show independent assortment if they are on the same chromosome? • Genes located close together on the same chromosome are said to display genetic linkage.