* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4.1 Living Things Inherit Traits in Patterns
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
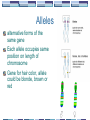
4.1 Living Things Inherit Traits in Patterns Mrs. Leos May 23, 2017 SO FAR…… We have learned that: Cells contain chromosomes NOW we will learn about: How genes for traits are passed from parent to offspring More about Gregor Mendel Dominant and recessive alleles Genetics The study of gene structure and the patterns of inheritance of traits from parent to offspring. Traits Inherited Hair color, eye color, blood type Traits passed from parent to child Acquired Ability to read, skills learned Genes Made of DNA Control traits that show up in an organism Sections of the chromosome shown here have been coloured in. Each section is a piece of DNA called a gene. Heredity Passing of traits (genes) from parent to offspring Alleles alternative forms of the same gene Each allele occupies same position on length of chromosome Gene for hair color, allele could be blonde, brown or red Multiple Alleles A trait is controlled by more than two alleles Blood Type A&B =AB Curly hair & straight hair= wavy hair Brown Eyes & Green Eyes =Hazel eyes Alleles are considered to be co-dominant Co-dominant-both show up Human Chromosome Number 46 Sex Chromosomes X-chromosome Y Chromosome XX=Girl XY=Boy Gregor Mendel- Father of Genetics Science of how trait are inherited through alleles 1856 studied garden peas for height, flower and pod position, seed shape, seed color, pod shape, pod color, flower color Mendel Success Mendel figured how traits were transmitted from parent to offspring. He did not know about DNA, genes or chromosomes Phenotype Actual characteristics that can be observed Physical trait that show up Examples:Height, size of feet How something looks Pheno=photo Genotype The genetic makeup of an organism, all the genes that an organism has Geno=gene Genotype not always obvious Principle of Dominant Dominant Allele -form that appears or shows up Covers up weaker form Recessive Allele –expressed in phenotype only when two copies of it are present in the genotype Form that seems to disappear Still carried by parent!! On page 18 Demonstration your understanding Write your summary