* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Probability and Punnett Squares
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
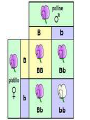
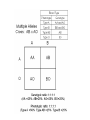
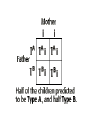
Probability and Punnett Squares Probability is a way of expressing knowledge or belief that an event will occur or has occurred. The likely hood of cross will produce a particular type of offspring Probability • Percentage- way of expressing a number as a fraction of 100 • Ratio- expression that compares quantities relative to each other • What is the % of heterozygous offspring? • What is the ratio of heterozygous to purple flowers? Co-Dominance • With codominance, a cross between organisms with two different phenotypes produces offspring with a third phenotype in which both of the parental traits appear together. Incomplete Dominance • With incomplete dominance, a cross between organisms with two different phenotypes produces offspring with a third phenotype that is a blending of the parental traits. Polygenic • Means multiple alleles coding for a single gene. • Ex- hair color Epistasis • When the affects of one gene suppress the expression of another gene Sex linked • Sex linked genes is the phenotypic expression of an allele that is related to the chromosomal sex of the individual. This mode of inheritance is in contrast to the inheritance of traits on autosomal chromosomes, where both sexes have the same probability of expressing the trait. Since, in humans, there are many more genes on the X than there are on the Y, there are many more X-linked traits than there are Y-linked traits. Multiple alleles • Although any individual has at most two different alleles, most genes exist in a large number of allelic forms in the population as a whole. In some cases, the alleles have different effects on the phenotype, and their dominance interactions with each other can be described as a series. Blood System • For example, the best known human blood groups, the ABO system, comprises three sets of alleles at the I locus, IA, IB, and IO. The first two are dominant to the latter: that is, the AA and AO genotypes produce indistinguishable blood group phenotypes, called “Type A”, as do BB and BO, which produce “Type B” blood.