* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download video slide - Downtown Magnets High School
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
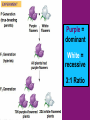
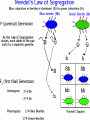
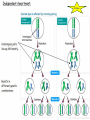
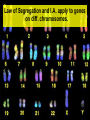
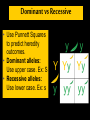
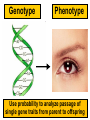
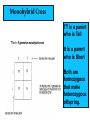
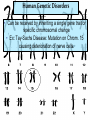
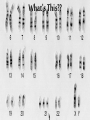
Mendel and His InGene-ius Idea… Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit, and respond to info essential to life processes. Essential Knowledge • 3A3: The chromosomal basis of inheritance provides an understanding of the pattern of passage of genes from parent to offspring. •… “particulate” hypothesis is the idea that parents pass on discrete heritable units (genes)… Gregor Mendel 1822-1884 Mendel’s Peas… • Planned experiments using characters (flower color) and traits (purple/white) He Experiments… • Mendel mated 2 contrasting, true-breeding varieties hybridization • True-breeding parents = P generation • Hybrid offspring of P generation = F1 generation • When F1 individuals self-pollinate = F2 generation is produced Purple = dominant White = recessive 3:1 Ratio Mendel’s heritable factor = gene Alternate versions =alleles IA Video Law of Segregation and I.A. apply to genes on diff. chromosomes. • Genes near each other on same chromosome tend to move as a unit • Probability of segregation is a fxn of the distance b/t them. Dominant vs Recessive • Use Punnett Squares to predict heredity outcomes. • Dominant alleles: Use upper case. Ex: S • Recessive alleles: Use lower case. Ex: s • Homozygous: alleles for a trait are same. Ex: SS or ss or TT (true breeding) • Heterozygous: alleles for a trait are different. Ex: Ss or Tt Ratios • Receive 2 types of info: genotype and phenotype. • Genotype: genetic trait that you cannot see (genes) • Phenotype: trait or behavior you can see physically. Genotype Phenotype Use probability to analyze passage of single gene traits from parent to offspring Punnett Squares!! One Factor Punnett Square • One trait = monohybrid cross. • Ex: Cross a tall dominant homozygous pea plant (TT) w/ short recessive homozygous pea plant (tt). Monohybrid Cross TT is a parent who is Tall tt is a parent who is Short Both are homozygous that make heterozygous offspring. Ratios to Know TT x tt = 100% Dominant, but heterozygous Tt x Tt = 75% Dominant, 25% Recessive, 3:1 Two factor Punnett Square • Cross 2 traits = dihybrid cross. • Example: Cross a dominant green, smooth pea plant (GGSS) with a recessive yellow, wrinkled pea plant (ggss) Ratios to Know SsTt x SsTt = 9:3:3:1 9 dominant in both traits 3 dominant in one trait or the other trait 1 recessive for both traits Human Genetic Disorders • Can be received by inheriting a single gene trait or specific chromosomal change • Ex: Tay-Sachs Disease: Mutation on Chrom. 15 causing deterioration of nerve cells. What’s This?? Punnett Square Sample Probs