* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt presentation
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
RNA-binding protein wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
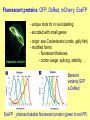
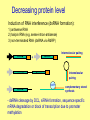
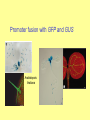
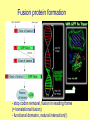
Gene function analyses, Reporter genes in direct and reverse genetics Reporter genes • encode proteins that can be directly visualized or enzymes, whose activity can be visualized • quantitative or qualitative assessment • promoter activity analyses, subcellular localization of proteins, optimizing transformation procedure, …. Constrains: - background (autofluorescence, natural enzyme activity within the tissue) - protein stability (mask changes in promoter activity) - degradation of fusion proteins Reporter genes gene product substrate detection gusA b-glucuronidase (E. coli) luc gfp luciferase (fire fly) green fluorescent protein (gelly fish) MUG X-gluc luciferin xxx fluorescence histochemical luminiscence fluorescence Fluorescent proteins: GFP, DsRed, mCherry, EosFP - unique tools for in vivo labelling - encoded with small genes Aequoria victoria - origin: sea Coelenterata (corals, gelly fish) - modified forms: - fluorescent features, - codon usage, splicing, stability, … Barevné varianty GFP a DsRed EosFP – photoactivatable fluorescent protein (green to red FP) GUS Qualitative detection (X-gluc) • oxidized blue precipitate of reaction product • low background • slow diffusion • mostly in fixed material (X-gluc = 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl glucuronide) Quantitative detection (MUG) • GUS enzyme isolation, fluorimetric statement • highly sensitive, low background (MUG = 4-methylumbelliferyl-beta-D-glucuronide) Gene function analyses Modulation of expression: - increased protein level (overexpression) – introduction of a gene with a strong constitutive promoter - alt. gain-of-function mutations - decreased protein level by RNAi - alt. loss-off-function mutation Tilling – point mutation in commercial collections Reporter gene fusions Decreasing protein level Induction of RNA interference (dsRNA formation): 1) antisense RNA 2) hairpin RNA (e.g. sense-intron-antisense) 3) non-terminated RNA (dsRNA via RdRP) Intermolecular pairing + intramolecular pairing RdRP complementary strand synthesis - dsRNA cleavage by DCL, siRNA formation, sequence specific mRNA degradation or block of transcription due to promoter methylation Promoter analysis Fusion of analyzed promoter with reporter gene (transcription fusion), with or without the original transcript: reportérový gen P gen T - usually introduction of new copy into the genome Indicates: - tissue, organ, developmental specificity - responses to external factors Confirmation with other approaches advisible (risk of artifacts) Promoter fusion with GFP and GUS Arabidopsis thaliana Fusion protein formation - stop codon removal, fusion in reading frame (= translational fusion) - functional domains, natural interaction(!) GFP fusion proteins - Protein localization analyses, protein interactions - in vivo labelling of cellular structures Golgy complex chromosomes microtubules