* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint - The Science Queen
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
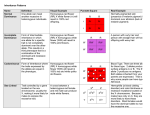
Whose got Genes? Genes, Heredity, & DNA Baker 2003/2004 What are genes? Genes are a segment of DNA on a chromosome that controls a particular trait. Genes are located on the chromosomes in the nuclei. Each organims has a fixed number of chromosomes. Humans have 23 pairs (46) chromosomes. Genetics is the study of how traits are passed on from one generation to another Baker 2003/2004 So what is DNA? DNA is a complex molecule (polymer) found in all living things. The primary function of DNA is to store and transmit genetic information that tells cells which proteins to make and when to make them. Baker 2003/2004 DNA TRIVIA An idea about size: An average cell nucleus is about 6 micrometers in diameter. The total length of the DNA in the human genome is 1.8 meters. There must be several levels of coiling and super coiling in DNA Baker 2003/2004 Who was Gregor Mendel? Baker 2003/2004 Who was Gregor Mendel? Austrian monk who studied mathematics and science As a boy he could predict the possible types of flowers and fruits that would result from crossbreeding two plants in his father’s garden Baker 2003/2004 Who was Gregor Mendel? Curiosity about the connection between the color of a pea flower and the type of seed that same plant produced inspired him to begin experimenting with garden peas in 1856. Made careful use of scientific methods, which resulted in the first recorded study of how traits pass from one generation to the next. Baker 2003/2004 What is GENETICS? Baker 2003/2004 What is GENETICS? The study of how traits are inherited through the interactions of genes. Baker 2003/2004 What is a GENE? Baker 2003/2004 What is a GENE? The material that controls which traits are expressed in an organism Genes come in pairs and offspring inherit one copy of each gene from each parent Baker 2003/2004 Define the following terms: Heredity Allele Trait Baker 2003/2004 Define HEREDITY The passing of traits from parent to offspring Baker 2003/2004 Define ALLELE The different forms of a trait that a gene may have One form of a gene Baker 2003/2004 Define TRAIT Ways of looking, thinking, or being Traits that are genetic are passed down through the genes from parents to offspring Baker 2003/2004 Describe RECESSIVE Baker 2003/2004 Describe RECESSIVE A trait that is covered over, or dominated, by another form of that trait and seems to disappear Hidden when the other copy of the gene contains the dominant allele. A recessive allele shows up only when there is no dominant allele present Shown with a lower-case letter Baker 2003/2004 What is HOMOZYGOUS? Baker 2003/2004 What is HOMOZYGOUS? Both alleles [forms of the gene] are the same When offspring inherit two dominant genes, (one dominant gene from each parent) they are said to be homozygous dominant When offspring inherit two recessive genes, (one recessive gene from each parent) they are said to be homozygous recessive Baker 2003/2004 What is HETEROZYGOUS? Baker 2003/2004 What is HETEROZYGOUS? When alleles occur in different forms When offspring inherit one dominant gene and one recessive gene, they are said to be heterozygous Since the dominant gene will be expressed, they are said to be heterozygous dominant Baker 2003/2004 Describe DOMINANT Baker 2003/2004 Describe DOMINANT A trait that covers over, or dominates, another form of that trait Trait that always shows up, even when only one of the two alleles is in the dominant form Shown by a capital letter Baker 2003/2004 Define GENOTYPE Baker 2003/2004 Define GENOTYPE An organism's genetic makeup Baker 2003/2004 Define PHENOTYPE Baker 2003/2004 Define PHENOTYPE Outward physical appearance and behavior of an organism Baker 2003/2004 What is a PUNNETT SQUARE? A tool to predict the probability of certain traits in offspring that shows the different ways alleles can combine A way to show phenotype & genotype A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result when genes are crossed Baker 2003/2004 What is a PUNNETT SQUARE? Letters stand for dominant and recessive alleles An uppercase letter stands for a dominant allele Lowercase letters stand for recessive alleles Baker 2003/2004 Introduction to Punnett Squares: A Punnett Square is a chart drawn to determine the probable results of a genetic cross. To be able to draw a Punnett Square, you must know the genotype of both parents. R R r r RR Rr RR rr Baker 2003/2004 Punnett Squares Sample Problem 1. In roses, red flowers are dominant over white flowers. What are the possible offspring when a homozygous red rose is crossed with a homozygous white rose. Baker 2003/2004 Generation 1 homozygous red rose = RR homozygous white rose = ww Baker 2003/2004 Generation 2 homozygous red rose = RR heterozygous red rose = Rw homozygous white rose = ww Baker 2003/2004 Generation 3 homozygous red rose = RR heterozygous red rose = Rw homozygous white rose = ww Baker 2003/2004 List the 3 Principles of Heredity Baker 2003/2004 List the 3 Principles of Heredity Traits are controlled by alleles on chromosomes An allele’s effect is dominant or recessive When a pair of chromosomes separate during meiosis the different alleles for a trait move into separate sex cells Baker 2003/2004 References Slideshow adapted from http://www.scienceclass.net/PowerPoints/Genetics.htm Baker 2003/2004