* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pedigree Charts Introduction
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
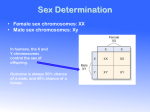
PEDIGREE CHARTS A family history of a genetic condition Quick Review • Genotype = what genes someone has • Genes are usually represented by a letter, a capital letter for the dominant trait, a small case for the recessive. • Example: Tongue Rolling is dominant, so we use R to represent the tongue rolling • Inablility to roll your tongue is recessive so we use r to represent the non-rolling gene • For every trait, you get a gene from each parent Genotypes and Phenotypes • Mom and Dad are Rrthat is their genotype, they can also be described as heterozygous-they have 1 of each gene • What is their PHENOTYPE? (Roller or non-roller?) • The youngest son has a genotype of rr-he is Homozygous recessive-2 copies of the recessive gene • His phenotype? What is a pedigree chart? • Pedigree charts show a record of the family of an individual • They can be used to study the transmission of a hereditary condition • They are particularly useful when there are large families and a good family record over several generations. Studying human genetics • Pedigree charts offer an ethical way of studying human genetics (Because you cannot make certain individuals breed in order to study genetics.) • Today genetic engineering has new tools to offer to doctors studying genetic diseases • A genetic counsellor will still use pedigree charts to help determine the distribution of a disease in an affected family Symbols used in pedigree charts • • • • • A marriage with five children, two daughters and three sons. The next to eldest son is affected by the condition. Normal male Affected male Normal female Affected female Marriage Eldest child Youngest child Symbols • Shaded individuals have the trait you’re studying • Boys = squares • Girls = circles • Married-connected at side • Siblings-connected at TOP not at the side (hopefully not siblings AND married) • Oldest child-to the left • Question-if shaded individuals in this pedigree have blue eyes, what is the GENOTYPE of the parents? Other Symbols • Divorced, separated • Deceased • Identical twins • Fraternal twins Organising the pedigree chart • A pedigree chart of a family showing 20 individuals Organising the pedigree chart – Generations are identified by Roman numerals I II III IV Organising the pedigree chart • Individuals in each generation are identified by Arabic numerals numbered from the left • Therefore the affected individuals are II3, IV2 and IV3 I 1 II III IV 2 3 4 5 6 7 What’s Going On? Shaded = Blue Eyes • 1 and 2 split after having 4, 2 then had kids with 3 and split with her too after 5-9 were born • Genotypes of 1, 4,7? • Genotypes of 2 & 3? • Genotypes of 5,6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12? Time to Practice… 1. Complete the practice worksheet on pedigrees in class in pairs (we will review) 2. Pedigree activity – you will be the geneticist trying to figure out the pattern of inheritance for different traits, disorders, or diseases.