* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NO OXYGEN!
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
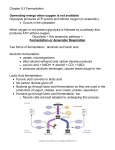
BIOLOGY Chapter 4.6 Fermentation SB3. Students will derive the relationship between single-celled and multi-celled organisms and the increasing complexity of systems. a. Explain the cycling of energy through the processes of photosynthesis and respiration. b. Compare how structures and function vary between the six kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protists, fungi, plants, and animals). c. Examine the evolutionary basis of modern classification systems. d. Compare and contrast viruses with living organisms. KEY CONCEPT Fermentation allows the production of a small amount of ATP without oxygen. OH NO! NO OXYGEN! WHAT DO WE DO? • If no oxygen is available, cells can obtain energy through the process of anaerobic respiration. • A common anaerobic process is fermentation. • Fermentation is not an efficient process and results in the formation of far fewer ATP molecules than aerobic respiration. There are two primary fermentation processes: 1. Lactic Acid Fermentation 2. Alcohol Fermentation Lactic acid fermentation occurs when oxygen is not available. For example, in muscle tissues during rapid and vigorous exercise, muscle cells may be depleted of oxygen. They then switch from respiration to fermentation. The pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is broken down to lactic acid and energy is released (which is used to form ATP). Glucose → Pyruvic acid → Lactic acid + energy GLYCOLYSIS AEROBIC ANAEROBIC When oxygen levels are too low aerobic animals become anaerobic and produce lactic acid. this causes muscle cramps. LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION: PYRUVIC ACID BECOMES LACTIC ACID •The process of lactic acid fermentation replaces the process of aerobic respiration so that the cell can have a continual source of energy, even in the absence of oxygen. •However this shift is only temporary and cells need oxygen for sustained activity. Lactic acid that builds up in the tissue causes a burning, painful sensation. Alcohol fermentation occurs in yeasts and some bacteria. Pyruvic acid formed during glycolysis is broken down to produce alcohol and carbon dioxide and is released (which is used to form ATP). FERMENTATION ALCOHOL LACTIC ACID ALCOHOLIC FERMENTATION: PYRUVIC ACID BECOMES ALCOHOL AND CO2 Fermentation allows glycolysis to continue. • Fermentation allows glycolysis to continue making ATP when oxygen is unavailable. • Fermentation is an anaerobic process. –occurs when oxygen is not available for cellular respiration –does not produce ATP Glucose → Pyruvic acid → alcohol + carbon dioxide + energy • Fermentation allows glycolysis to continue making ATP when oxygen is unavailable. • NAD+ is recycled to glycolysis • Lactic acid fermentation occurs in muscle cells. – glycolysis splits glucose into two pyruvate molecules – pyruvate and NADH enter fermentation – energy from NADH converts pyruvate into lactic acid – NADH is changed back into NAD+ Fermentation and its products are important in several ways. • Alcoholic fermentation is similar to lactic acid fermentation. – glycolysis splits glucose and the products enter fermentation – energy from NADH is used to split pyruvate into an alcohol and carbon dioxide – NADH is changed back into NAD+ – NAD+ is recycled to glycolysis Fermentation is used in food production. –yogurt –cheese –bread Fermentation is used in food production. – Yogurt - Soy Sauce – Cheese - Vinegar –Bread - Olives/ Pickles – Beer/ Meade - Wine/ Ale – Sauerkraut - Malt Lactic Acid or Alcohol Fermentation? EITHER WAY ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION ONLY PRODUCES 2 ATP. AEROBIC RESPIRATION USES OXYGEN TO MAKE MUCH MORE ATP