* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA and Mutations Power Point
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
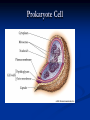
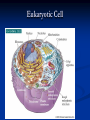
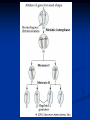
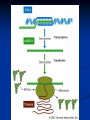
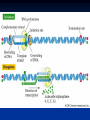
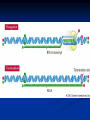
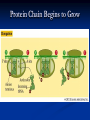
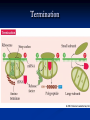
DNA, Mutations and Hazardous Waste Prokaryote Cell Eukaryotic Cell Chromosomes DNA Structure Nucleotides Make up Nucleic Acid nucleotide= nitrogenous base + phosphate group + sugar Bases DNA= A,T, G, C Bases RNA= A, U, G, C Pairs A-T(U), G-C ALWAYS Central Dogma Theory DNA replication- DNA to DNA DNA transcription- DNA to RNA (transcribe genes into RNA, junk DNA does not need to transcribe or gets deleted after transcription) Translation- RNA into protein (uses 3 types of RNA to get proteins made!) Messenger RNA Begins Translation at a Ribosome Genetic Code Determines Amino Acid Protein Chain Begins to Grow Termination Point Mutations Point mutations are changes in single bases silent mutations occur when the amino acid that it codes for doesn't change due to the DNA mutation missense mutations cause an amino acid substitution (sicklecell anemia), these mutations may reduce or disable protein function codon has a point or shift change that causes the translation process to be terminated too early frame-shift is when a single-base is inserted or deleted in a gene this has the potential of changing most of the codons and associated amino acids Chromosomal Mutations- Deletion Chromosomal Mutation- cont. Chromosomal Mutations cont. Chromosomal Mutations- cont. Other Mutagenic Terms Mutagen- any chemical or physical agent that induces a genetic mutation or increases the mutation rate Teratogen- any substance, agent, or process that interferes with normal prenatal development causing one or more developmental abnormalities in the fetus. Carcinogen- a substance or agent that causes the development or increases the incidence of cancer Causes of Cancer More than 80% of cases of cancer are attributed to cigarette smoking, exposure to carcinogenic chemicals, ionizing radiation, and ultraviolet rays; overexposure to the sun is the major cause of skin cancer. Mutations can be spontaneous or induced When would a mutation be spontaneous? When would a mutation be induced? Mutations can be detrimental, neutral or occasionally beneficial Detrimental Neutral Beneficial Think Evolution and Natural Selection- DNA mutations are necessary for this to occur!