* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CH 5 CQ
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
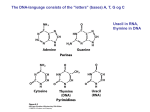
CLICKER QUESTIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Click to edit Master title style Large Biological Molecules Click to edit Master subtitle style Questions prepared by Jung Choi Georgia Institute of Technology © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Which group of large biological molecules is not synthesized via dehydration reactions? a) polysaccharides b) lipids c) proteins d) nucleic acids © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Which polysaccharide has the greatest number of branches? a) cellulose b) chitin c) amylose d) amylopectin e) glycogen © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Why are human enzymes that digest starch unable to digest cellulose? a) Cellulose is made of amino-containing sugars that cannot be metabolized. b) Cellulose contains L-glucose instead of D-glucose; starchdigesting enzymes are specific for polymers of D-glucose. c) Cellulose has beta-glycosidic linkages; starch-digesting enzymes cleave only alpha-glycosidic linkages. d) Cellulose has beta-galactoside linkages that only bacterial beta-galactosidases can cleave. e) Cellulose fibers are covalently cross-linked; starch-digesting enzymes cannot cleave these cross-links. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Diversity among Biological Macromolecules Which type of biological polymer has the least diversity in physicochemical properties and structure? a) polysaccharides b) polypeptides c) DNA d) RNA © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Lipids All lipids a) are made from glycerol and fatty acids. b) contain nitrogen. c) have low energy content. d) are acidic when mixed with water. e) do not dissolve well in water. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Lipids Compared to tropical fish, arctic fish oils have a) more unsaturated fatty acids. b) more cholesterol. c) fewer unsaturated fatty acids. d) more trans-unsaturated fatty acids. e) more hydrogenated fatty acids. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Subunits If actively growing cells are fed 14C-labeled glucose, what macromolecules will become radioactive first? a) proteins b) starch c) nucleic acids d) fatty acids © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Subunits and Metabolic Labeling If you want to selectively label nucleic acids being synthesized by cells, what radioactive compound would you add to the medium? a) 35S-labeled sulfate b) 32P-labeled phosphate c) 14C-labeled leucine d) 3H-labeled thymidine e) 14C-labeled © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. guanine Protein Structure and Amino Acids Sickle-cell disease is caused by a mutation in the betahemoglobin gene that changes a charged amino acid, glutamic acid, to valine, a hydrophobic amino acid. Where in the protein would you expect to find glutamic acid? a) on the exterior surface of the protein b) in the interior of the protein, away from water c) at the active site, binding oxygen d) at the heme-binding site © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Protein Structure The sickle-cell hemoglobin mutation alters what level(s) of protein structure? a) primary b) tertiary c) quarternary d) all of the above e) primary and tertiary structures only © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Macromolecular Structures and Bonds Ceviche is prepared by marinating fresh raw fish in citrus juice for several hours, until the flesh becomes opaque and firm, as if cooked. How does citrus juice render the seafood safe to eat? a) Acidic pH denatures (unfolds and inactivates) proteins by disrupting their hydrogen bonds. b) Citrus juice denatures proteins by disrupting their ionic bonds. c) Citrus juice contains enzymes that hydrolyze peptide bonds to break apart proteins. d) Citrus juice dissolves cell membranes by disrupting hydrophobic interactions. © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. RNA and DNA How does RNA differ from DNA? a) DNA encodes hereditary information; RNA does not. b) DNA forms duplexes; RNA does not. c) DNA contains thymine; RNA contains uracil. d) all of the above © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.